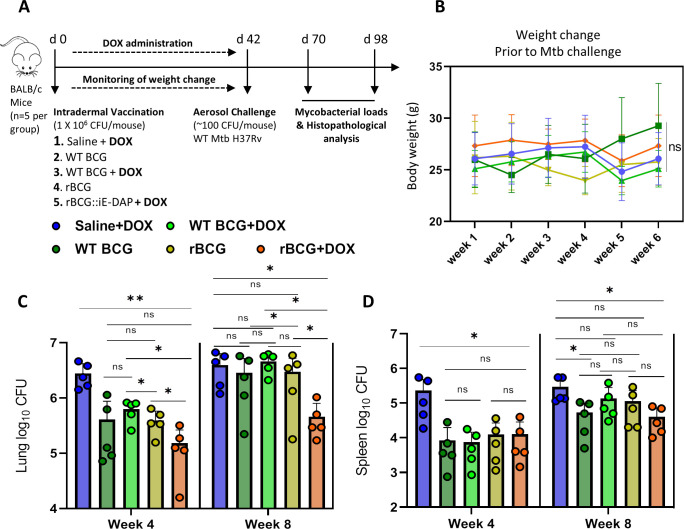
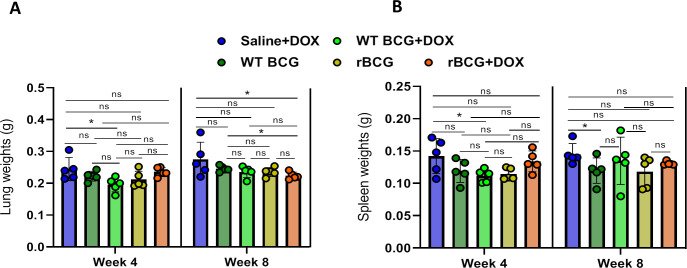
Figure 4. Efficacy of rBCG::iE-DAP in comparison to standard WT BCG for protection against Mtb H37Rv infection in mice.
(A) Schematic representation of the mouse immunization and Mtb H37Rv challenge protocol. (B) Percentage weight change at week 6 (day 42) immediately prior to Mtb challenge. (C, D) Lung and Spleen bacterial burdens at week 4 and week 8 post-challenge with Mtb. Five mice per group (n=5) were used for the in vivo experiments. Student t-test was used for statistical analysis. The error bars represent the standard deviation relative to the mean. *: p-value <0.05, **: p-value <0.01.