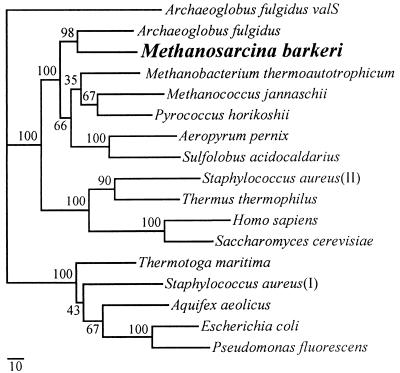
FIG. 1.
Phylogeny of the M. barkeri IleS protein. The standardized, exponentially weighted consensus tree of the 500 most parsimonious trees, evaluated by maximum-likelihood analysis, is shown. A percentage at a node represents the relative-likelihood support for that branch, as calculated by the TreeCons program. The tree was rooted using the valS gene of A. fulgidus. The scale bar represents the estimated number of substitutions per 100 amino acid positions along each branch. The Swiss Protein database accession numbers of the sequences used are, from top to bottom, O28059 (A. fulgidus valS), O29622 (A. fulgidus), P26499 (M. thermoautotrophicum), Q58357 (M. jannaschii). P46215 (S. acidocaldarius), P41368 (S. aureus II, a plasmid-encoded copy that confers PAr). P56690 (T. thermophilus), P41252 (H. sapiens), P09436 (S. cerevisiae), P46213 (T. maritima), P41972 (S. aureus I, genomic copy), P46207 (A. aeolicus), P00956 (E. coli), and P18330 (P. fluorescens). The A. pernix and P. horikoshii sequences were from the respective genome databases.