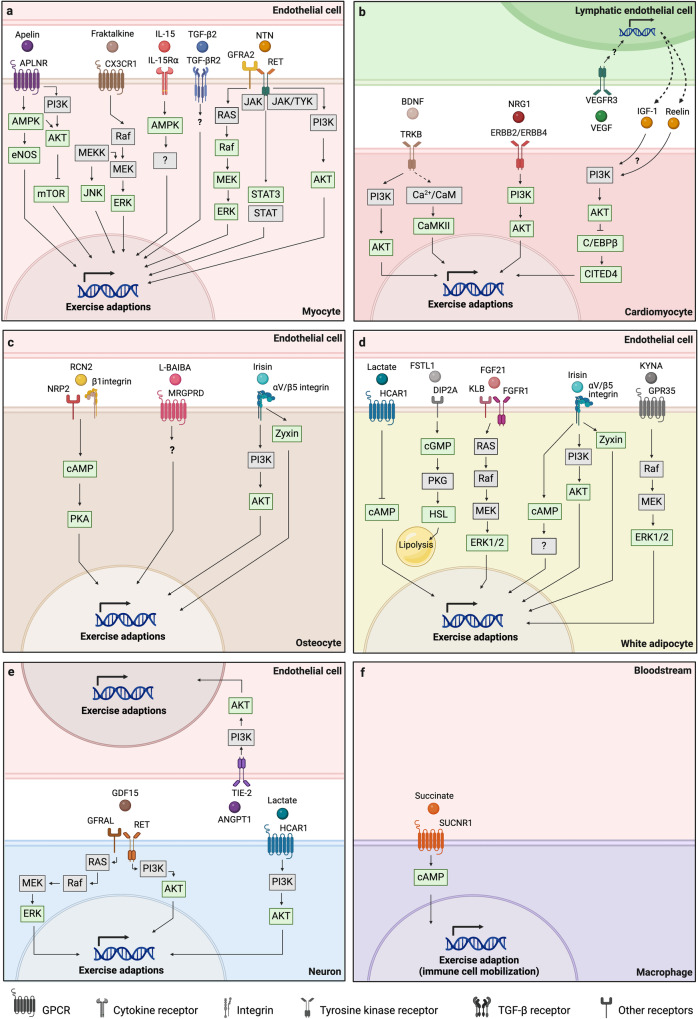
Fig. 3.
Overview of exerkine receptors and downstream signaling pathways investigated in animal studies. Autocrine, paracrine, and endocrine mobilization makes exerkines available for exerkine receptors localized on distinct target cells including myocytes (a), cardiomyocytes (b), lymphatic endothelial cells (b), osteocytes (c), white adipocytes (d), neurons (e), and macrophages (f). Binding of exerkines to their target receptor triggers tissue-specific signaling cascades and adaption processes with potential therapeutic effects in different diseases. Downstream mediators of exerkine signaling that were investigated in vivo are highlighted in green. APLNR apelin receptor, CX3XR1 C-X3-C motif chemokine receptor 1, IL-15Rα Interleukin-15 receptor α, IL-15 Interleukin 15, TGF-βR2 transforming growth factor β receptor 2, GFRA2 Glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor family receptor α 2, RET REarranged during Transfection, NTN Neurturin, TRKB Tropomyosin-related kinase B, BDNF Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, NRG1 Neuregulin 1, ERBB2/ERBB4 Erb-B2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase 2/ Erb-B2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase 4, VEGFR3 Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3, VEGF Vascular endothelial growth factor, IGF-1 Insulin-like growth factor 1, NRP2 Neuropilin 2, RCN2 Reticulocalbin 2, FSTL1 Follistatin-like 1, DIP2A Disco-interacting protein 2 homolog A, HSL hormone sensitive lipase, MRGPRD Mas-related G protein-coupled receptor type D, L-BAIBA β-aminoisobutyric acid, HCAR1 Hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 1, FGFR1 Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1, KLB Co-receptor β-Klotho, FGF21 Fibroblast growth factor 21, GPR35 G protein-coupled receptor 35, KYNA Kynurenic acid, GFRAL Glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor family Receptor α Like, GDF15 Growth differentiation factor 15, TIE-2 Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor TEK, ANGPT1 Angiopoietin 1, SUCNR1 Succinate receptor 1. Created with BioRender.com