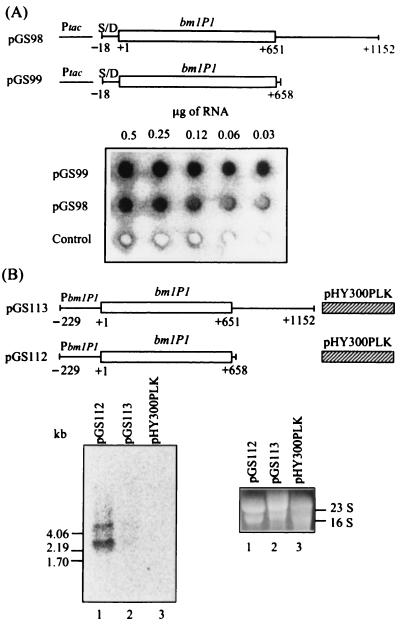
FIG. 4.
Dot blot and Northern blot analyses of relative levels of the bmlP1 transcripts. (A) Dot blot analysis. Total cellular RNA was isolated from E. coli cells carrying plasmid pGS98 or pGS99 or the control vector pKK223-3 and grown in the presence of IPTG. After serial twofold dilutions, RNA was loaded onto a nylon membrane and probed with a 0.65-kb 32P-labeled DNA fragment corresponding to the bmlP1 coding region. Similar results were obtained from two independent experiments. Ptac, tac promoter; S/D, putative ribosome-binding site of bmlP1. (B) Northern blot analysis. Total cellular RNA extracted from B. megaterium cells carrying plasmid pGS112 or pGS113 or the control vector pHY300PLK during mid-exponential-phase growth was denatured, subjected to electrophoresis on a formaldehyde–1% agarose gel, and transferred to a nylon membrane. The membrane was then hybridized with a 0.65-kb 32P-labeled single-stranded DNA complementary to the upper strand of the bmlP1 coding region. Similar results were obtained from two independent experiments. PbmlP1, bmlP1 promoter. The migration positions of the single-stranded RNA markers (New England BioLabs, Inc.) are indicated. The lower right panel shows the ethidium bromide-stained rRNA on the gel used for Northern blotting.