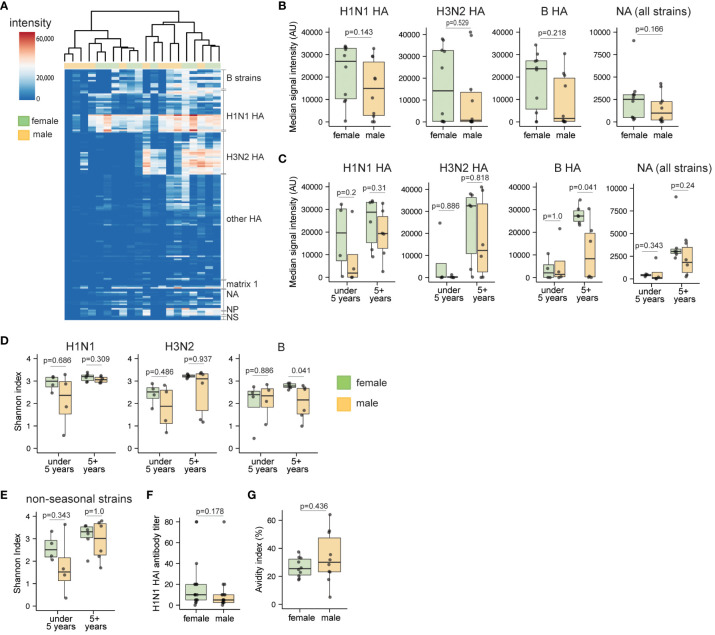
Figure 4.
Sex differences in breadth and diversity of influenza-specific antibodies in children in response to LAIV. Culture supernatants from unstimulated and LAIV-stimulated tonsil organoids (n=20, 10 male and 10 female children, age-matched) were collected on day 10 and antibody breadth and diversity were assessed using a high throughput protein microarray. (A) Heatmap representing signal intensities for influenza-specific IgG antibodies elicited by LAIV in the tonsil organoids. (B) Protein microarray antibody summary data for influenza virus subtypes. Data represent the median signal intensity for antibodies binding all H1N1 HA, H3N2 HA, B HA, and NA proteins from the array. (C) Median antibody signal intensities stratified by donor sex and age. Shannon index for influenza-specific IgG antibodies binding (D) seasonal and (E) non-seasonal virus subtypes. (F) A/California/07/2009 H1N1 virus neutralizing antibody titers in LAIV-stimulated tonsil organoids (n=35) from day 7 supernatants. (G) Antibody avidity index of LAIV 2019-20 vaccine HA-specific antibodies on day 10 after LAIV stimulation (n=20). Each point is an individual donor. Mann Whitney U tests were performed to determine the statistical significance between groups. Boxplots indicate the median value, with hinges denoting the first and third quartiles and whiskers denoting the highest and lowest value within 1.5 times the interquartile range of the hinges.