Figure 1.
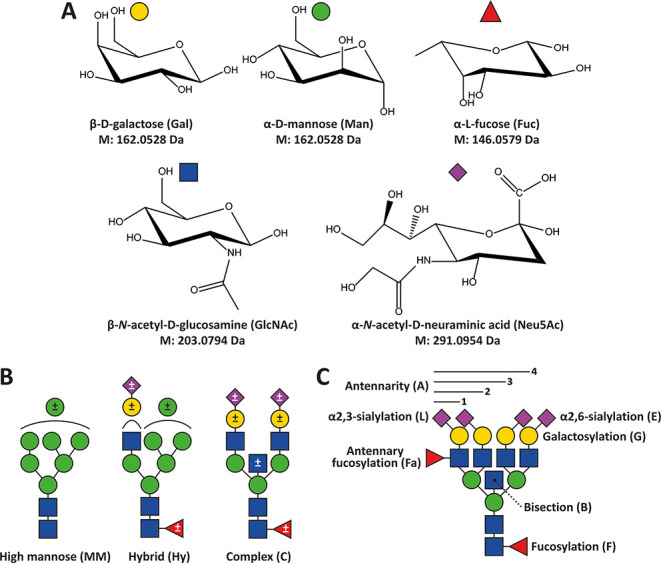
Monosaccharide diversity and glycan types characterizing human N-glycans with illustrative examples of glycosylation traits calculated therefrom. (A) Common monosaccharide constituents of human blood protein-associated N-glycans and their monoisotopic residue mass. (B) General types of N-glycans in humans. Optional modifications are indicated by ± in the symbols. Neuraminic (sialic) acids can be either α2,3- or α2,6-linked. Other potential modifications include phosphorylation, sulfation, sialic acid acetylation, or LacdiNAc repeats. (C) Glycosylation traits used to describe N-glycans in this study. Sialic acids with undefined linkages are denoted with the abbreviation S throughout.
