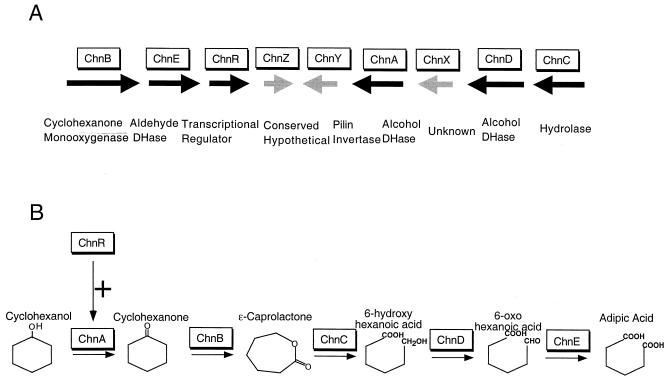
FIG. 5.
Functional assignment of genes in the cyclohexanol oxidation pathway. (A) Identification of the essential genes for conversion of cyclohexanol to adipic acid. The genetic organization of the nine genes on the 14-kb insert of pDCQ2 is illustrated. Black arrows, six genes shown to be essential for conversion of cyclohexanol to adipic acid; gray arrows, three genes that are not essential for the conversion. Direction of arrows indicates direction of transcription of the genes. Enzymes encoded by the genes are in boxes above the corresponding genes. (B) Assignment of the biochemical function of the six genes essential for conversion of cyclohexanol to adipic acid. Five of the essential genes encode enzymes, and one encodes a regulatory protein. The five steps of the reactions are represented by horizontal arrows. The enzymes (boxes) are assigned to each required reaction based on GC/MS results (Table 3). The vertical arrow with the plus sign represents positive regulation of the first step of the reaction by the transcriptional regulator ChnR.