Fig. 3.
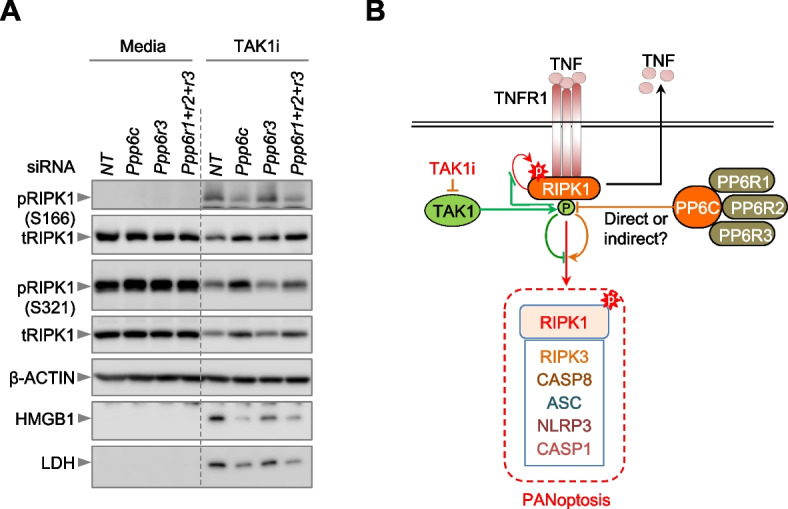
The PP6 complex negatively regulates inhibitory phosphorylation of RIPK1 to drive PANoptosis. A Immunoblots for S166 and S321 phospho-RIPK1 (pRIPK1) and total RIPK1 (tRIPK1) using cell lysates and immunoblots for high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) using culture supernatants from bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) treated with TAK1 inhibitor (TAK1i) for 8 h. Blots were re-probed for β-ACTIN to serve as the internal loading control. The blots presented are representative of three independent experiments. NT: non-targeting siRNA; Ppp6r1+r2+r3: BMDMs treated with siRNAs against Ppp6r1, Ppp6r2, and Ppp6r3. B Schematic illustrating the potential mechanism for the PP6 complex to drive TAK1i-induced, RIPK1-dependent PANoptosis in BMDMs. The phosphorylation (P) marks denote the RIPK1 S166 (red, spiked) and S321 (green, rounded) phosphorylations
