Figure 1.
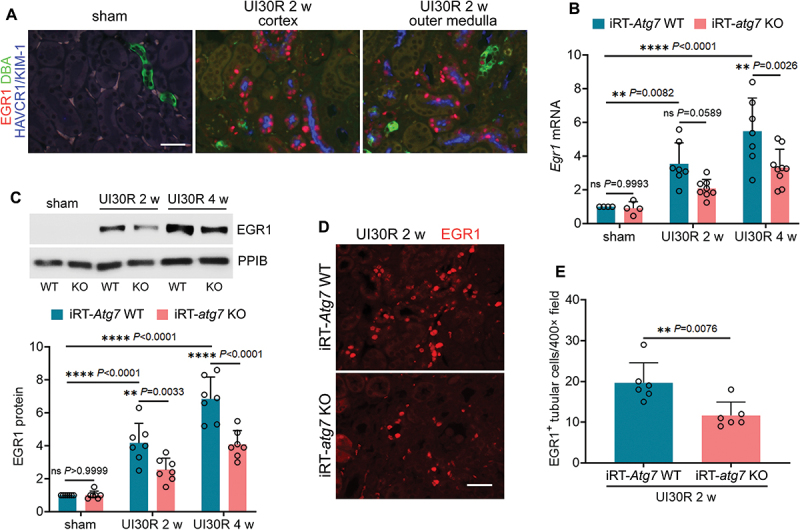
Autophagy deficiency inhibits EGR1 in renal tubular cells during maladaptive kidney repair after ischemic AKI in mice. (A) C57BL/6 mice underwent sham operation (n = 3) or 30-min unilateral renal ischemia followed by reperfusion for 2 weeks (n = 3). Left kidneys were harvested for co-immunofluorescence of EGR1 (red) and HAVCR1/KIM-1 (blue). Fluorescein-DBA (green) was used as a marker for renal distal tubules. Scale bar: 20 µm. (B-E) WT and iRT-atg7 KO mice underwent sham operation or 30-min unilateral renal ischemia followed by reperfusion for up to 4 weeks. Left kidneys were harvested. (B) RT-qPCR of Egr1 mRNA (sham: n = 4; UI30R 2 w: WT n = 7, KO n = 8; UI30R 4 w: WT n = 7, KO n = 9). (C) EGR1 immunoblot and densitometry (n = 7 for each group). PPIB/cyclophilin B was used as an internal loading control. (D) EGR1 immunofluorescence. Scale bar: 20 µm. (E) quantification of EGR1-positive tubular cells (n = 6 for each group). Data in (B), (C) and (E) are presented as mean ± SEM. For statistics, two-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used for (B) and (C). 2-tailed, unpaired Student t-test was used for (E).
