Figure 9.
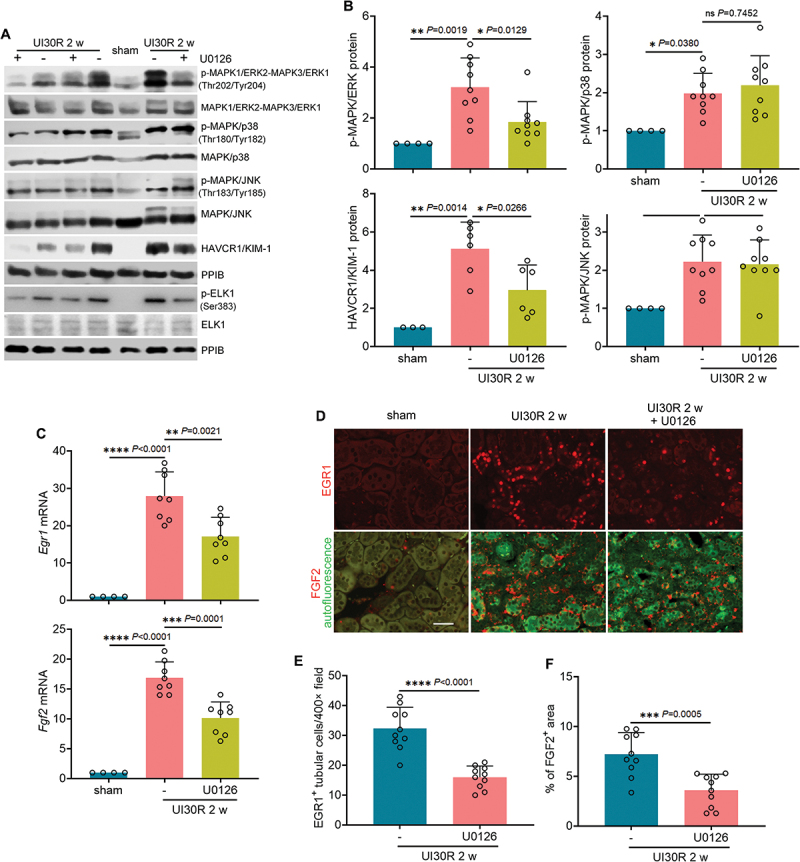
Inhibition of MAPK1/ERK2-MAPK3/ERK1 suppresses EGR1 and FGF2 in renal tubules during maladaptive kidney repair after ischemic AKI in mice. C57BL/6 mice underwent sham operation (n = 4) or 30-min unilateral renal ischemia followed by reperfusion alone (n = 11) or with U0126 (n = 10) (20 mg/kg, i.P., every other day injection, starting from day 2 of reperfusion) for 2 weeks. Left kidneys were harvested. (A) immunoblot of p-MAPK1/ERK2-MAPK3/ERK1 (Thr202/Tyr204), MAPK1/ERK2-MAPK3/ERK1, p-MAPK/p38 (Thr180/Tyr182), MAPK/p38, p-MAPK/JNK (Thr183/Tyr185), MAPK/JNK, HAVCR1/KIM-1, p-ELK1 (Ser383) and ELK1. (B) densitometry of p-MAPK1/ERK2-MAPK3/ERK1 (Thr202/Tyr204), p-MAPK/p38 (Thr180/Tyr182), p-MAPK/JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) and HAVCR1/KIM-1 immunoblot. (C) RT-qPCR of Egr1 and Fgf2 mRNA. (D) immunofluorescence of EGR1 and FGF2. Scale bar: 20 µm. (E) quantification of the numbers of EGR1-positive tubular cells. (F) quantification of FGF2-positive staining areas. Data in (B), (C), (E) and (F) are presented as mean ± SEM. For statistics, one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used for (B) and (C). 2-tailed, unpaired Student t-test was used for (E) and (F).
