Figure 4. Direct, excitatory monosynaptic connection between the medulla and phrenic motoneurons.
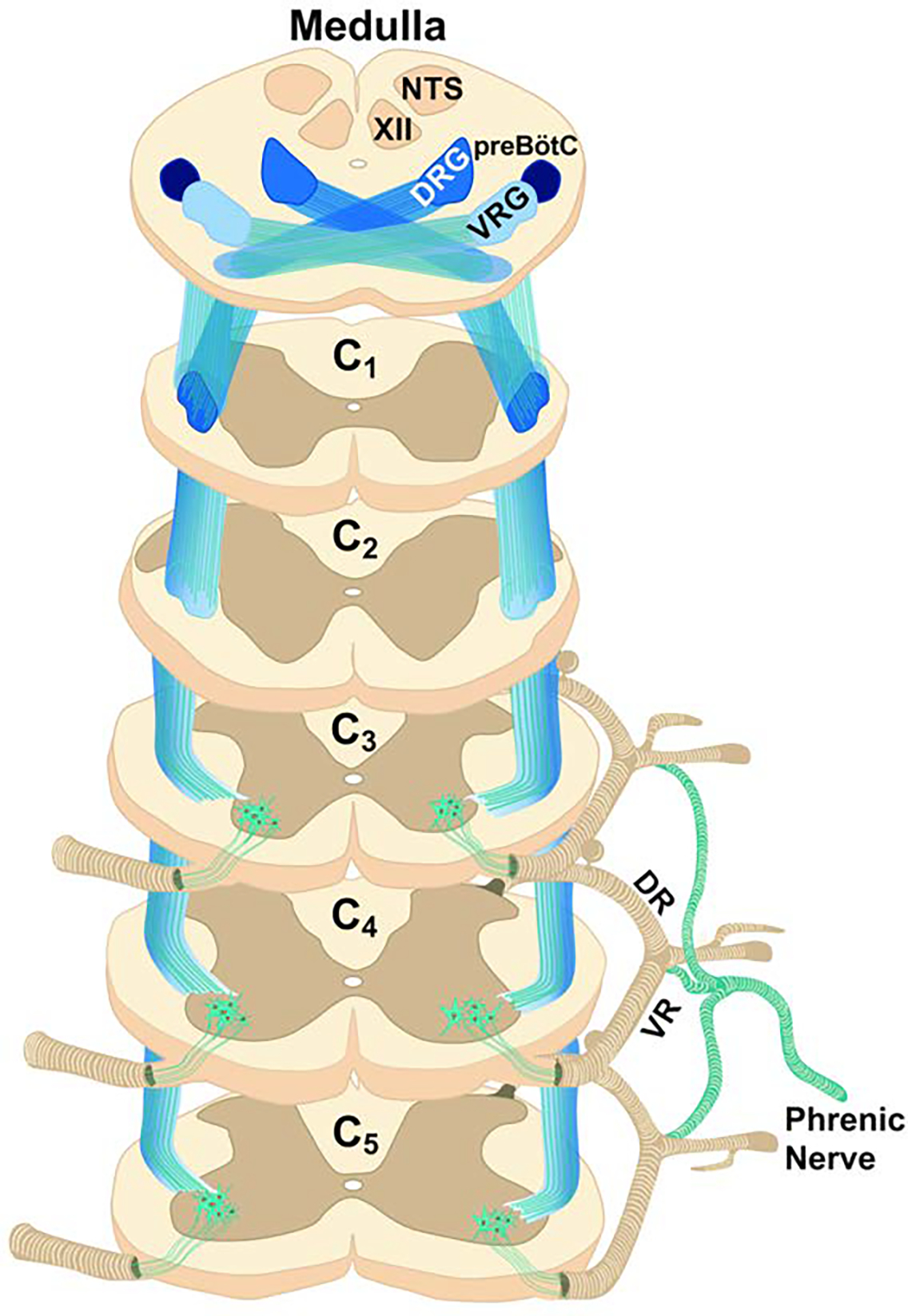
The illustrated synaptic projections provide the primary “inspiratory drive” which depolarize phrenic motoneurons during inspiration, and thereby trigger diaphragm contraction. The axons of these projections travel in lateral and ventral cervical funiculi (the image illustrates the ventro-lateral funiculus). As noted in the text, PhrMNs also receive monosynaptic inhibitory inputs from the Bötzinger complex in the medulla. VRG: ventral respiratory group; DRG: dorsal respiratory group; XII: hypoglossal motor nucleus; NTS: nucleus of the solitary tract; preBôtC: pre-Bötzinger complex
