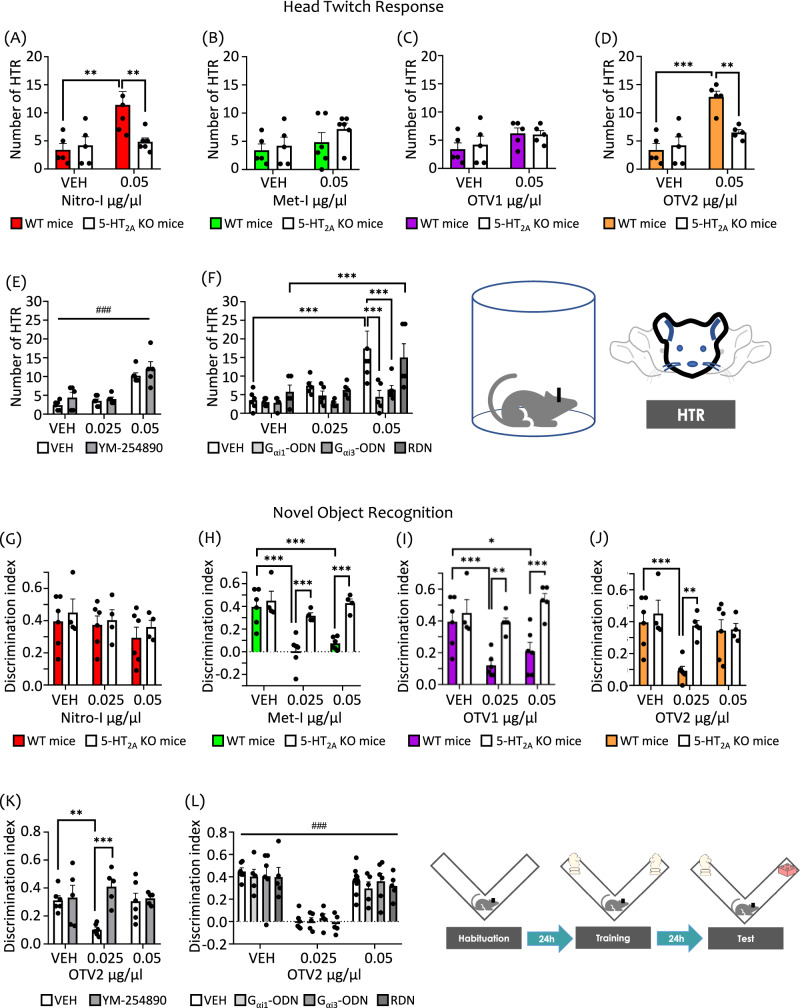
Fig. 4. Head twitch response (HTR) and long-term novel object recognition (NOR).
HTR in wild-type (WT) and 5-HT2AR knockout (KO) mice following ICV administration of (A) Nitro-I, (B) Met-I, (C) OTV1, and (D) OTV2, or vehicle (VEH). The increase in HTR induced by Nitro-I and OTV2 at the dose of 0.05 µg/µl was absent in KO mice. E ICV administration of YM-254890 (16 µM) did not modulate the increase in HTR induced by OTV2 at the dose of 0.05 µg/µl. F ICV administration of specific antisense oligonucleotides (ODN), Gαi1-ODN, Gαi3-ODN, but not control random oligonucleotides (RDN) blocked HTR induced by OTV2 at the dose of 0.05 µg/µl. NOR memory test in WT and 5-HT2AR KO mice following ICV administration of (G) Nitro-I, (H) Met-I, (I) OTV1, and (J) OTV2 or vehicle (VEH). In WT mice, Met-I and OTV1 induced memory deficits at the dose of 0.025 and 0.05 µg/µl, and OTV2 was effective only at the dose of 0.025 µg/µl. These effects were abrogated in KO mice. Nitro-I did not trigger memory deficits at any of the doses tested. K YM-254890 (16 µM) abrogated the memory deficits induced by OTV2 at the dose of 0.025 µg/µl. L ICV administration of Gαi1-ODN, Gαi3-ODN, or the control RDN sequence did not modulate the memory deficits induced by OTV2 at the dose of 0.025 µg/µl. The data represent mean ± SEM. The number of mice used in the experiments (n) corresponds to the individual points in the graph. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ###p < 0.001 (main effect of treatment). Two-way ANOVAs followed by Fisher’s post-hoc test.