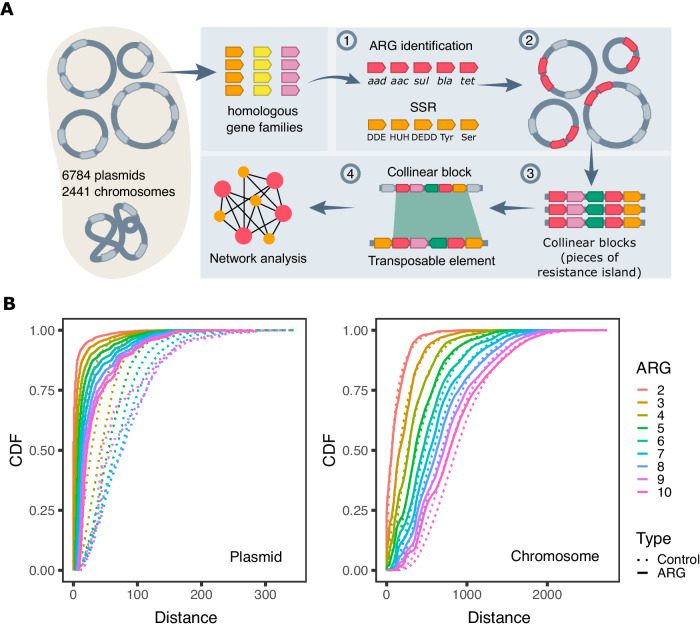
Fig. 1. Antibiotic resistance genes cooccur in plasmids in dense resistance islands.
A An illustration of our workflow for detecting resistance islands in plasmid genomes. Arrow boxes correspond to genes. (1) Protein-coding genes in bacterial genomes were clustered into gene families. ARGs and SSR genes were identified. (2) Significant cooccurrence tests for ARG pairs were conducted per replicon type in each genus. (3) Collinear syntenic blocks (CSBs) including coARGs were identified across genomes and (4) further compared to previously recognized transposable elements by sequence similarity (see Methods for additional clarifications). (B) Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) plots show that the distance between ARGs is shorter than the distance between a control group of randomly sampled genes in plasmids (left), but not in chromosomes (right). Intergenic distances were calculated by counting the number of protein-coding genes between two, and up to ten, adjacent ARGs. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.