Figure 2.
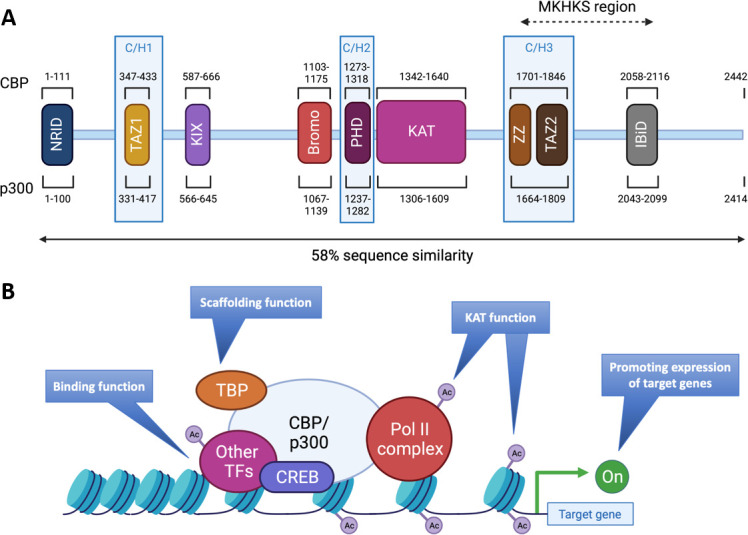
Structures and functions of CBP/p300. (A) The proteins CBP and p300 are composed of 2442 amino acids (AA) and 2414 AA, respectively, with 58% of sequence similarity within their domains. The various domains are represented by their position in the AA sequence: N-terminal nuclear receptor interaction domain (NRID or RID), cysteine-histidine rich region 1 (C/H1) containing the transcriptional adapter zinc finger 1 (TAZ1), kinase-inducible domain (KID) interacting domain (KIX), Bromodomain, C/H2 containing a plant homeodomain (PHD), lysine acetyltransferase domain (KAT), C/H3 containing the zinc finger (ZZ) and TAZ2 domains and interferon-binding transactivation domain (IBiD). The Menke-Hennekam syndrome (MKHKS) region corresponds to the location of the missense variants leading to the MKHKS. (B) CBP and p300 act as transcriptional co-activators of target genes by different mechanisms: (1) Binding function by facilitating the physical and functional interactions of TF; (2) scaffolding function allowing the recruitment of TF and in particular CREB; (3) KAT function by catalysing the transfer of acetyl groups on lysine residues of both histone tails and non-histone proteins such as the RNApolII complex and TF. Ac, acetyl group; TBP, TATA binding protein; TF, transcription factors. Adapted from a study by Van Gils et al.15
