Figure 4.
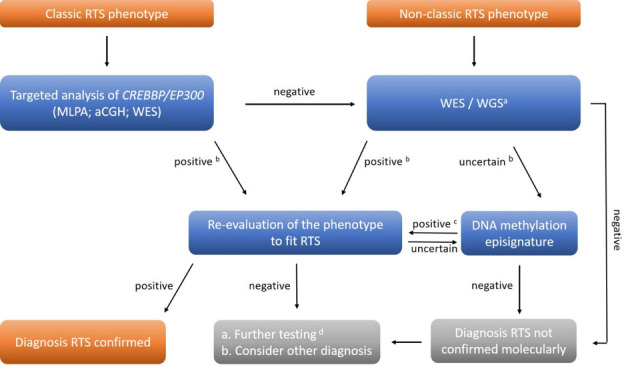
Molecular diagnostic pathways for Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome. In individuals with clinically classic RTS phenotype, the first-line molecular diagnostic approach is targeted analysis of CREBBP and EP300 by Sanger sequencing and MLPA or by high throughput analysis (aCGH; WES). In individuals in whom RTS is not suspected, aCGH and WES or WGS are performed. a Including analysis of CREBBP / EP300 and genes causing related entities; b evaluation of results using ACMG classification23; c episignature specific for RTS24 ; d RNA studies; searches for mosaicism. aCGH, array Comparative Genomic Hybridisation; ACMG, American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics; MLPA, Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification; RTS, Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome; WES, whole-exome sequencing; WGS, whole-genome sequencing
