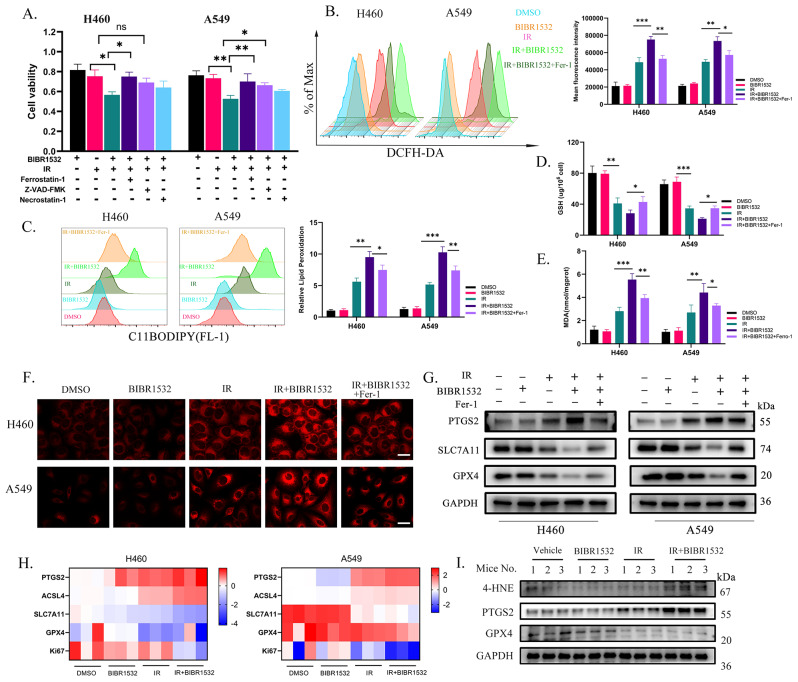
Fig. 3.
IR combined with BIBR1532 induced the increase of ROS in tumour cells and ferroptosis. A Cell viability of H460 and A549 cells to different cell death inhibitors (ferroptosis inhibitors, apoptosis inhibitors, and necrosis inhibitors) after treatment with BIBR1532 and IR was detected by CCK-8 assay. B, C DCFH-DA and C11-BODIPY were used to measure intracellular ROS and lipid peroxidation levels after exposure to IR (4 Gy) and BIBR1532 (20 µM for H460, 40 µM for A549) treatment. D, E NSCLC cells were pre-treated with or without BIBR1532, and cellular MDA and GSH levels were assessed after 4 Gy irradiation for 24 h. F After a 72-hour pretreatment with BIBR1532, cells were irradiated with or without 4 Gy for 48 h, and the intracellular Fe2+ concentration was evaluated through image and quantitative analysis. G Western blot analysis was conducted to measure the expression levels of PTGS2, SCL7A11, and GPX4 in H460 and A549 cells. H qRT-PCR was employed to determine the expression of ferroptosis-related genes in H460 and A549 cells. I The Western blot results indicated up-regulation of 4-HNE and PTGS2 expression and decreased GPX4 expression in the tumour tissue of mice treated with BIBR1532 in combination with IR. Each group was replicated three times, and the statistical data is presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001