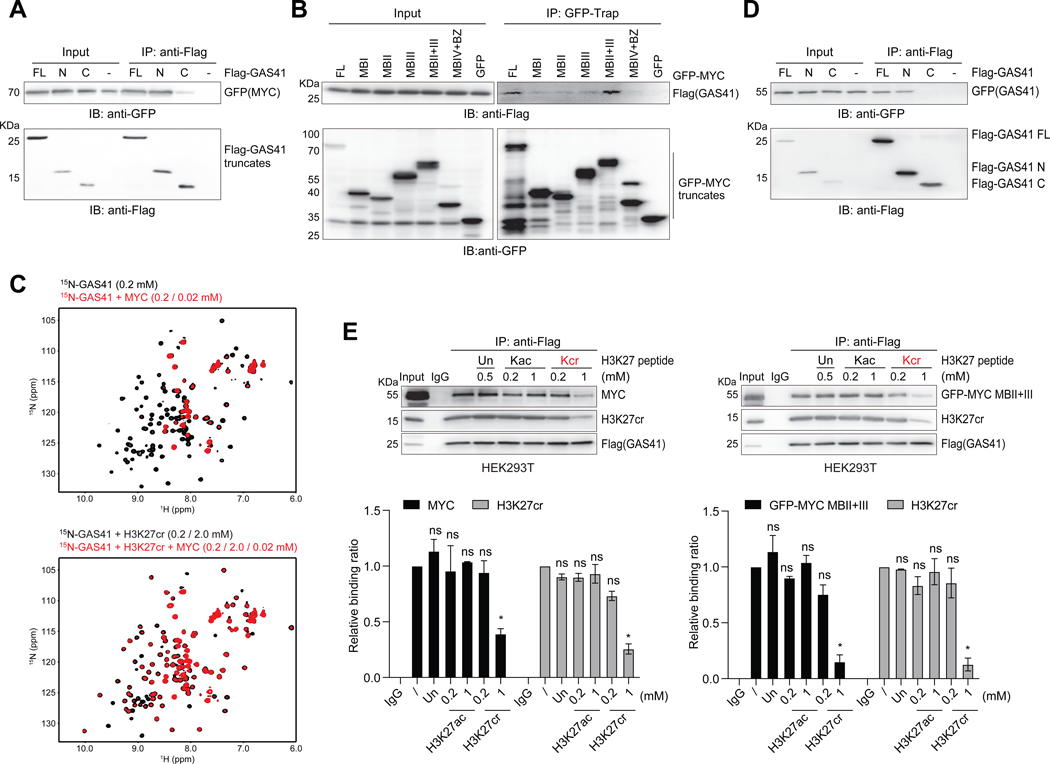
Figure 4. GAS41 YEATS domain interactions with H3K27cr and MYC.
(A) Co-IP of Flag-GAS41 full-length (FL; residues 1–227), N-terminal segment (N; residues 1–165) or C-terminal segment (C; residues 148–227) and IB with Flag and GFP antibodies assessing GAS41 interaction with MYC in HEK293T cells co-transfected with Flag-GAS41 and GFP-MYC.
(B) Co-IP of GFP-MYC and its various segments and IB with GFP and Flag antibodies in Flag-GAS41 and GFP-MYC co-transfected HEK293T cells.
(C) GAS41 YEATS domain binding to MYC (residues 1–262) (upper), or in the presence of the H3K27cr peptide (lower), as assessed by 2D 1H-15N HSQC spectra of the GAS41 YEATS domain.
(D) GAS41 dimerization, as assessed by Flag-GAS41 and GFP-GAS41 interaction in HEK293T cells, co-transfected with GFP-GAS41 and Flag-GAS41 of full-length, N- or C-terminal segment constructs, respectively. Cell lysate was subjected to Flag IP and followed by IB with antibodies against GFP.
(E) Western blot analysis and quantification of H3K27ac or H3K27cr peptide competition against Flag-GAS41 binding to MYC and H3K27cr in HEK293T cells. Varying amounts of H3K27, H3K27cr or H3K27ac peptide, as indicated, was added to the lysate of HEK293T cells, transfected with either Flag-GAS41 alone or together with GFP-MYC MBII+III, and followed by Flag IP and IB with antibodies against Flag, MYC, GFP, and H3K27cr. n=2.