Fig. 1. Generation and characterization of DPYSL2-B frameshift iPSCs.
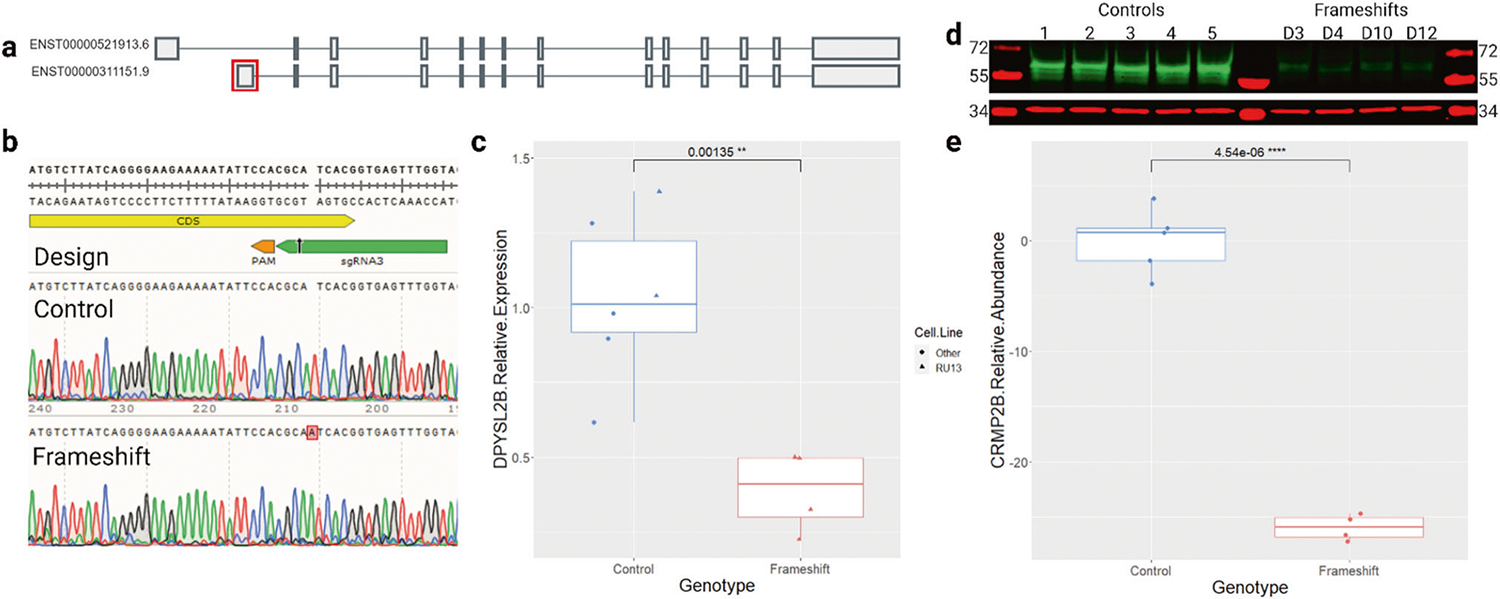
a DPYSL2 isoforms A (top) and B (bottom). The first exon of DPYSL2-B (boxed in red) was targeted to avoid impacting other transcripts. Image adapted from the GTEx portal. b Top panel shows sgRNA3 (green) and PAM (orange) used to create the frameshift mutation in the coding sequence (CDS, yellow) in exon 1. Bottom two panels show Sanger sequencing traces of DNA from control and frameshift iPSCs. c qRT-PCR results showing significantly reduced expression of DPYSL2-B in frameshift iPSC clones (n = 4) compared to control clones (n = 6 including 5 cell lines) (p = 0.001, t-test). Data were normalized to the geometric mean of GAPDH and β-actin loading controls, then to the average of the control clones. d Western blot comparing CRMP2-B (~64 kD, green) abundance in control (n = 5) and frameshift (n = 4) iPSC clones with GAPDH ( ~ 37 kD, red) as a loading control. e Quantification of (d) showing significantly reduced abundance of CRMP2-B in frameshift iPSCs compared to controls (p = 4.5 × 10−6, t-test). Data were normalized to GAPDH and then to the average of the control clones.
