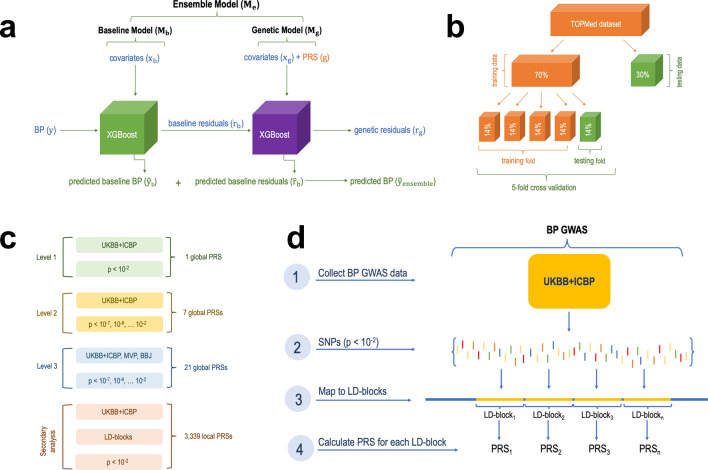
Figure 1.
Study design. (a) The proposed ensemble model framework. The ensemble is composed of two models. The baseline model, trained on covariates () only for prediction of SBP and DBP (). To assess the accuracy of the baseline model we calculated the residuals (baseline residuals ) by subtracting the predicted value of SBP/DBP from the actual value of SBP/DBP. The genetic model was trained on a subset of the covariates, and genetic components (global PRSs) for prediction of the baseline model residuals . We measured the accuracy of the genetic model by subtracting predicted genetic residuals from baseline residuals . The overall prediction of BP by the ensemble model is the sum of the predicted baseline BP (by the baseline model) and the predicted baseline residuals (by the genetic model). The accuracy of the ensemble model was assessed by calculating percent variance explained (PVE) by two models jointly. (b) The split of the primary, TOPMed dataset, into training and testing sets followed by the fivefold cross validation procedure where the training dataset is further split into 5 equal parts with one part designated for testing (repeated 5 times with 1/5 of the training data being designated at random for testing at each iteration). (c) Increasing levels of genetic models’ complexity where each new model included additional PRSs. (d) The process of calculating local PRSs per LD-blocks (secondary analysis). BBJ BioBank Japan, BP blood pressure, GWAS genome wide association study, LD linkage disequilibrium, Level model complexity level, MVP Million Veteran Program, P p-value threshold, PRS polygenic risk score, SNPs single-nucleotide polymorphisms, TOPMed Trans-Omics for Precision Medicine, UKBB + ICBP UK Biobank and International Consortium for Blood Pressure.