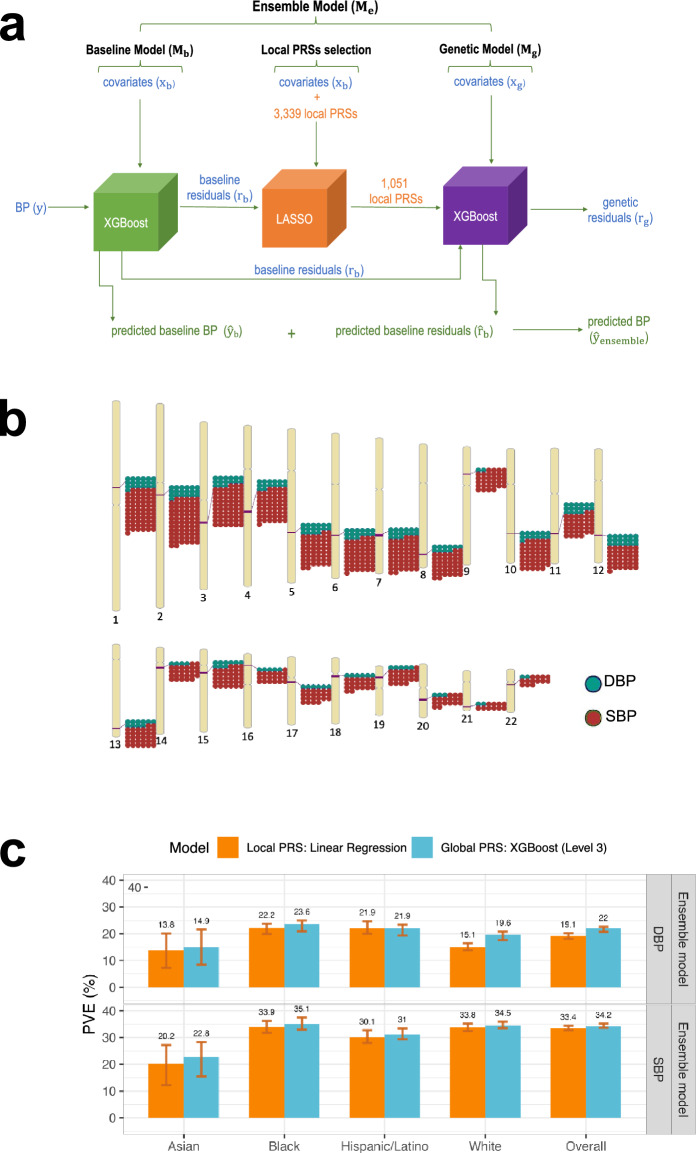
Figure 4.
Integration of LASSO feature selection tool into the ensemble model workflow. (a) The workflow of the ensemble model with the integration of the LASSO variable selection tool. To include local PRSs in the ensemble model while attempting to avoid overfitting, we added a LASSO selection step to the ensemble model development. As visualized, the residuals of the baseline model were used as the outcome in LASSO penalized regression with the local PRSs as features. LASSO substantially reduced the number of local PRSs (to 827 for SBP and 224 for DBP). The local PRSs selected by LASSO were then used as an input into the genetic model for prediction of the baseline residuals (). (b) Genomic locations of local PRSs, calculated over predefined LD-regions, selected by LASSO for SBP and DBP. (c) Comparison between the estimated PVE in the TOPMed test dataset for ensemble model Level 3 using global PRSs and the ensemble model using Linear regression and local PRSs. PVEs are reported for models of SBP and DBP, in the overall test dataset and stratified by self-reported race/ethnicity (White N = 10,877, Hispanic/Latino N = 3831, Black N = 3657, Asian N = 403 for DBP; White N = 10,823, Hispanic/Latino N = 3877, Black N = 3674, Asian N = 374 for SBP). The visualized 95% confidence intervals were computed as the 2.5% and 97.5% percentiles of the bootstrap distribution of the PVEs estimated over the test dataset. BP blood pressure, DBP diastolic blood pressure, LASSO least absolute shrinkage and selection operator, PRS polygenic risk score, SBP systolic blood pressure.