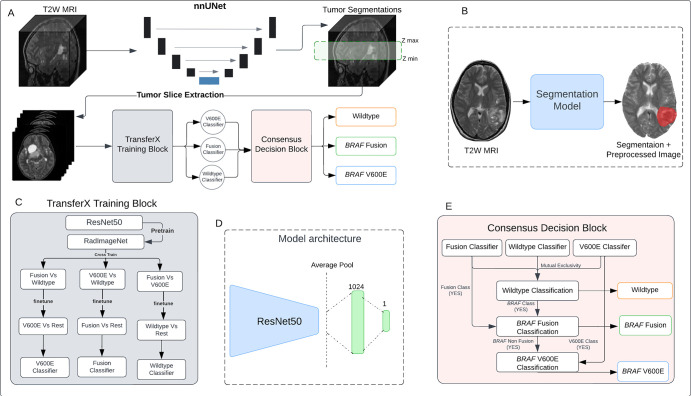
Figure 1:
(A) Schematic of the scan-to-prediction pipeline for molecular subtype classification. The pipeline inputs the raw T2-weighted (T2W) MRI scan and outputs the mutation class prediction. (B) Input and output depiction of the segmentation model from the first stage of the pipeline. The segmentation block also involves registration and preprocessing of the input scan. The output consists of the preprocessed input MRI scan along with the coregistered segmentation mask. (C) Flow diagram of the TransferX training block and approach. The TransferX algorithm is employed to train three individual subtype classifiers (BRAF wild type, BRAF fusion, and BRAF V600E). (D) The model architecture of the individual binary molecular subtype classifier. (E) Schematic of the consensus decision block. The block inputs the classification outputs and corresponding scores from the three individual subtype classifiers, fits them into a consensus logic, and outputs the final predictions. The mutational class predictions are output sequentially where the input is first checked for BRAF wild type or non-BRAF class first. If the input does not belong to a BRAF wild type or non-BRAF class, then the logic progresses to check the BRAF mutation class, with BRAF fusion checked first, followed by BRAF V600E.