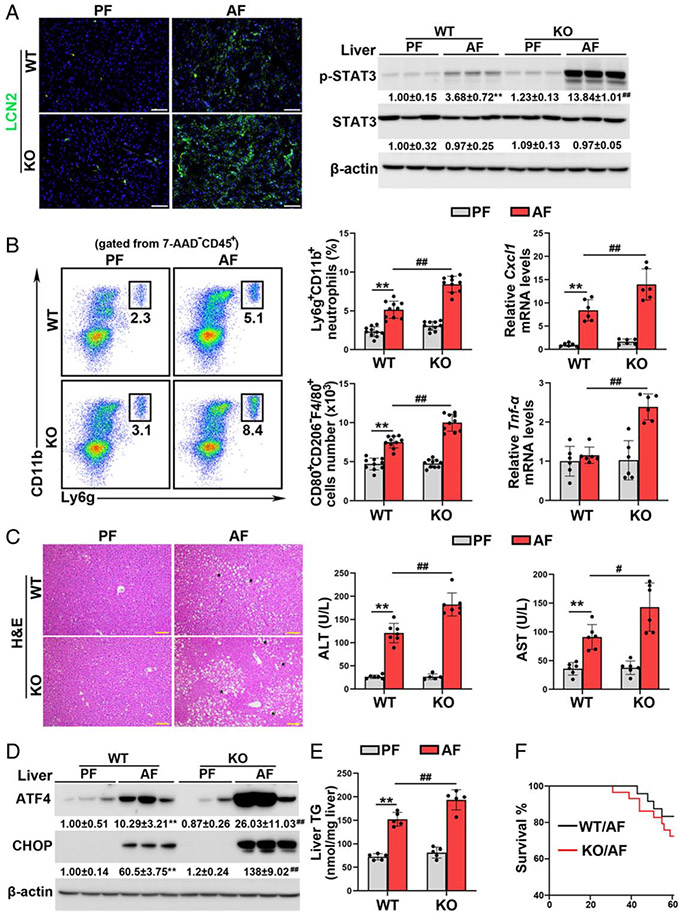
FIGURE 3.
The alcohol-induced hepatic inflammatory, steatosis, and ER stress were exacerbated in basic leucine zipper transcription factor ATF-like 3 (Batf3−/−) mice. (A) IF staining of lipocalin-2 (LCN2) (n = 7) and western blot analysis of p-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and STAT3 (n = 3) in the liver. (B) Hepatic neutrophils (n = 10), M1 macrophages (n = 10), and the mRNA levels of hepatic C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 9 (Cxcl1) and Tnf-α (n = 6). (C) Liver hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and plasma alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) activities (n = 5–7). Scale bars: 50 μm. Asterisks: lipid droplets. (D) Western blot analysis of hepatic activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) and C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) (n = 3). (E) Hepatic TG contents (n = 5). (F) Mouse survival rate. Data are presented as mean ± SD. **P < 0.01 versus wild-type (WT)/pair-fed (PF) mice; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 versus WT/alcohol-fed (AF) mice. ER indicates endoplasmic reticulum; IF, immunofluorescence; TG, triglyceride.