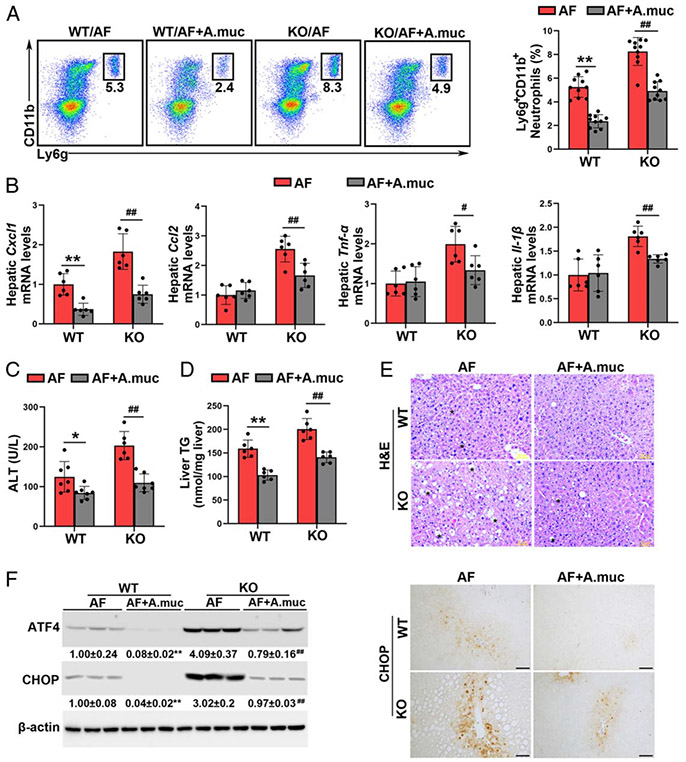
FIGURE 7.
Akkermansia muciniphila administration protects against alcohol-induced liver injury in both wild-type (WT) mice and Batf3−/− mice. Alcohol-fed C57BL/6J WT mice and Batf3−/− mice were administrated with or without A. muciniphila, respectively. (A) Representative dot plot and frequency of neutrophils in the liver (n = 10). (B) The mRNA levels of hepatic Cxcl1, Ccl2, Tnf-α, and Il-1β (n = 6). (C) Plasma alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels (n = 6–7). (D) Hepatic TG contents (n = 6). (E) Liver histopathological changes are shown by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. Scale bars: 50 μm. Asterisks: lipid droplets. (F) Hepatic ATF4 and CHOP protein levels (n = 3) and IHC staining of hepatic CHOP. Scale bars: 50 μm. Data are presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus WT/alcohol-fed (AF) mice; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 versus knockout (KO)/AF. IHC, immunohistochemistry; TG triglyceride.