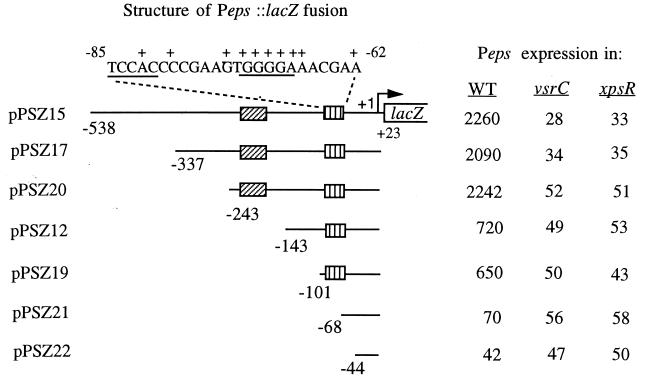
FIG. 1.
Identification of upstream regions involved in transcriptional regulation of Peps by VsrC and XpsR. The eps promoter and various lengths of upstream sequences were fused to lacZ on pRG970, generating plasmids pPSZ12 through pPSZ22. Plasmids were transferred into R. solanacearum wild-type (WT) strain AW, into strain AW-C, a vsrC mutant, and into strain AW-R164, an xpsR mutant. Peps expression (i.e., transcription directed by the Peps fragment) was monitored by measuring LacZ activity (given in Miller units [33]) in cells from cultures grown overnight in BG medium as described previously (4, 20). LacZ activity from cells harboring an empty pRG970 vector was 15. Nucleotide numbering is relative to the transcription start site of eps (21). The hatched boxes indicate the two important regions for activation of eps. The sequence at the top is that of the region identified by PCR mutagenesis as essential for transcription activation by xpsR and vsrC. +, positions of substitution mutations that reduced or eliminated activation of Peps (see Table 2). Underlined sequences, putative palindromic recognition sequences for VsrC. Values are averages from three experiments with <25% variation.