Fig. 1.
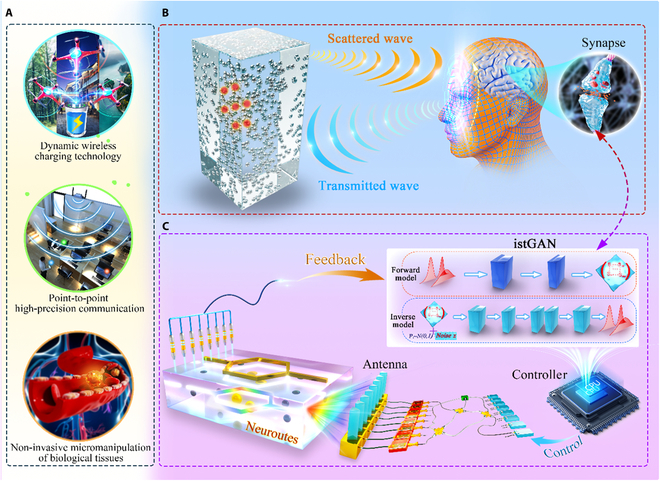
Illustration of the Neuroute concept inside dynamic scattering spaces. (A) Various applications, including dynamic wireless charging technology, point-to-point high-precision communication, and non-invasive micromanipulation of biological tissues, pose stringent demands for efficient information states’ acquisition inside dynamic scattering spaces. (B) The retina of human eyes transmits the perceptual information to neurons, and the nervous system controls the ciliary muscles for self-adaptive adjustment. Reversibly, when self-adaptive information states’ acquisition is carried out to multi-targets (shown by the red dot) in scattering spaces, the scattered wave can be analyzed by artificial synapses, and the transmitted wave can be controlled by the tunable perspective module. (C) Analogously, a controller embedded with an artificial neural network can be utilized to shape the wave field propagation routes by synthesizing scattering spaces, thus creating a neural route capable of transmitting information states on demand in a non-invasive and self-adaptive manner. This innovative approach is referred to as the Neuroute.
