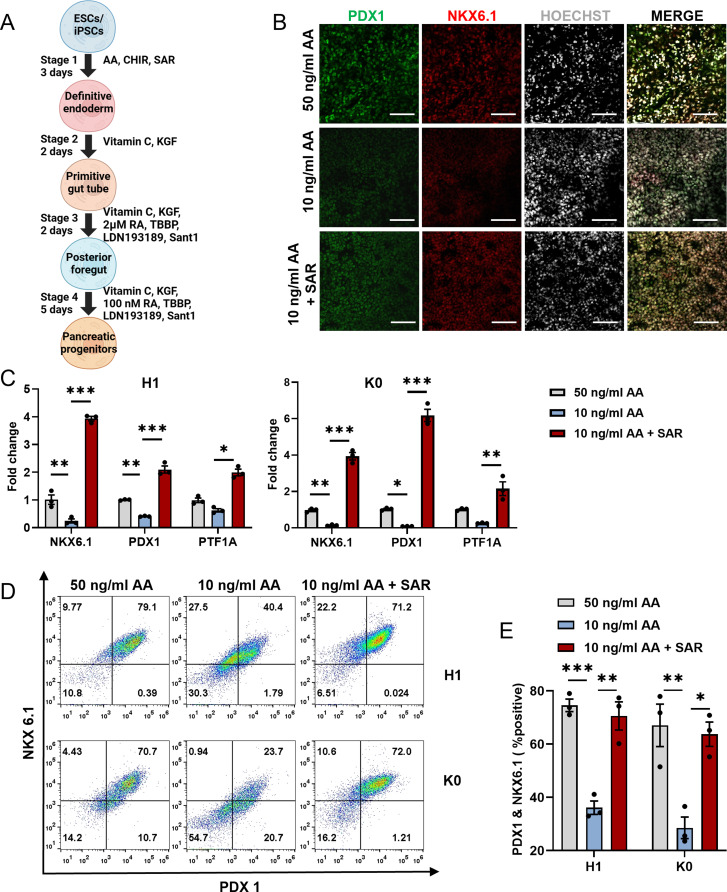
Fig. 8.
DE cells obtained from the AA-reduced differentiation protocol can further differentiate into pancreatic progenitor cells. (A) Schematic overview of pancreatic progenitor differentiation protocol for using SAR. (B) Human ESC line H1 was differentiated into DE cells using three different conditions: 50 ng/ml AA, 10 ng/ml AA, or 10 ng/ml AA combined with 0.5 µM SAR. Immunofluorescent staining was conducted to examine PDX1+ (green) and NKX6.1+ (red) cells derived from each condition during DE differentiation. The nucleus was counterstained with Hoechst 33,342. Scale bars = 100 μm. (C) QPCR analysis of NKX6.1, PDX1, and PTF1A expressions in pancreatic progenitor cells from human ESC line H1 and human iPSC line K0 derived from corresponding DE cells using three different conditions: 50 ng/ml AA, 10 ng/ml AA, or 10 ng/ml AA combined with 0.5 µM SAR. (D) Flow cytometric analysis of NKX6.1 and PDX1 in pancreatic progenitor cells differentiated from H1 and K0 cell. (E) Quantitative statistics of NKX6.1+/PDX1+ cells corresponding to (D). Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001