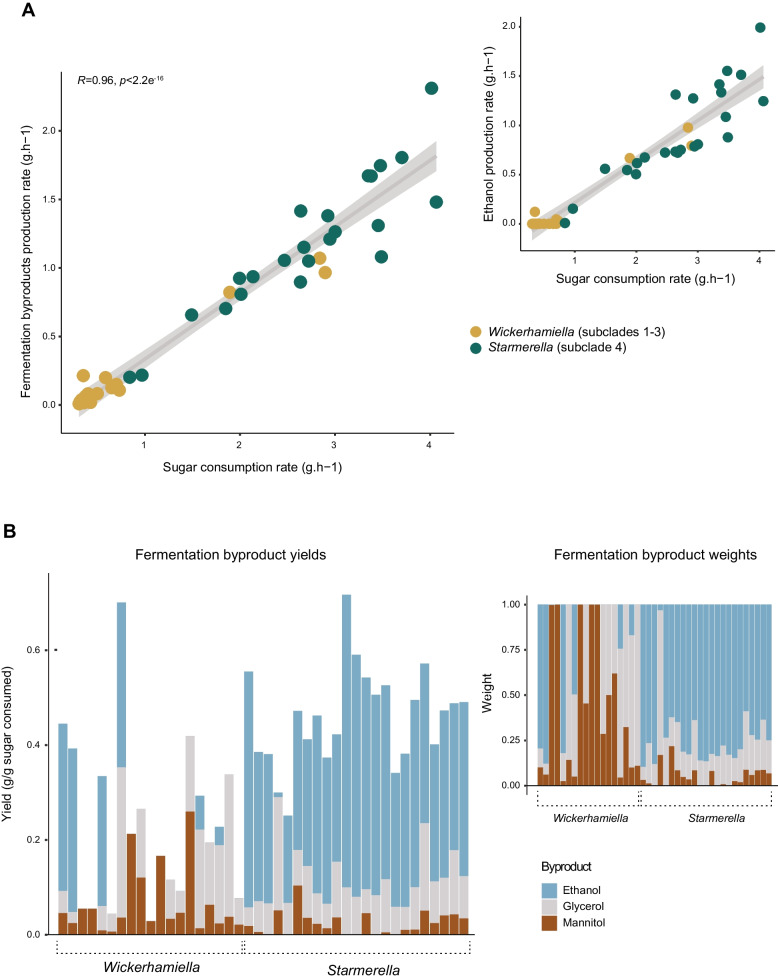
Fig. 2.
Comparison of respiration vs fermentation preferences across the W/S clade. A Correlation between maximum global fermentation byproduct production rates (ethanol, glycerol, and mannitol) and sugar consumption rates across the W/S clade, highlighting Wickerhamiella (subclades 1–3) and Starmerella (subclade 4) species in different colors. The inset (top, right) shows the correlation between sugar consumption rate and ethanol production rate determined at the same time points for the same species, denoting that the correlation is mainly driven by ethanol production. Each datapoint represents a single measurement for each species, but results for a replicate assay can be assessed in Additional file 6: Table S2 and Additional file 8: Fig S6A. B Fermentation byproduct (ethanol, glycerol, and mannitol) individual yields determined for each byproduct at the time point at which the maximum global yield was measured for each species (replicate assay can be assessed in Additional file 6: Table S2). The more pronounced bias towards fermentative metabolism in the Starmerella clade (subclade 4) when compared to Wickerhamiella (subclades 1–3) is noticeable. The manifest difference between Starmerella (subclade 4) and Wickerhamiella (subclades 1–3) concerning the main fermentation byproduct formed is highlighted in the inset (top, right) where the proportions of the three byproducts formed by each species are shown