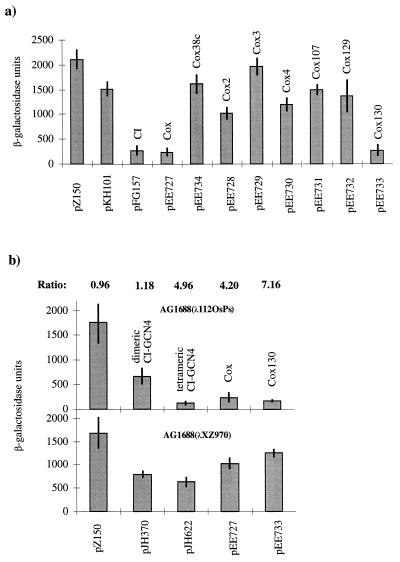
FIG. 3.
In vivo assays of dimerization and multimerization/cooperative binding of Cox. Each panel shows the results from three independent β-galactosidase measurements with pJH391 derivatives transformed in three different E. coli strains. (a) The dimerization in assay strain JH372. pZ150 (no CI repressor) and pKH101 (N terminus of the CI repressor) are negative controls. pFG157 (wild-type CI repressor) is the positive control. Wild-type Cox (pEE727), the truncated Cox (pEE734), and the different Cox mutants (pEE728 to pEE733) were analyzed and plotted against β-galactosidase units. (b) The multimerization/cooperative binding assay in strain AG1688(λ112OSPS) and in the control strain AG1688(λXZ970). β-Galactosidase assays were performed as in strain JH372. pJH370 (dimeric CI-GCN repressor) was used as the negative control. pJH622 (tetrameric CI-GCN modified repressor) is a positive control. pEE727 is the wild-type cox gene cloned in pJH391, and pEE733 contains the cox130 mutation. AG1688(λXZ970) is the strain used for detecting binding to the weak promoter-proximal operator only. The ratio between the values obtained in assay strain AG1688(λ112OSPS) and the control strain AG1688(λXZ970) is indicated above their respective columns.