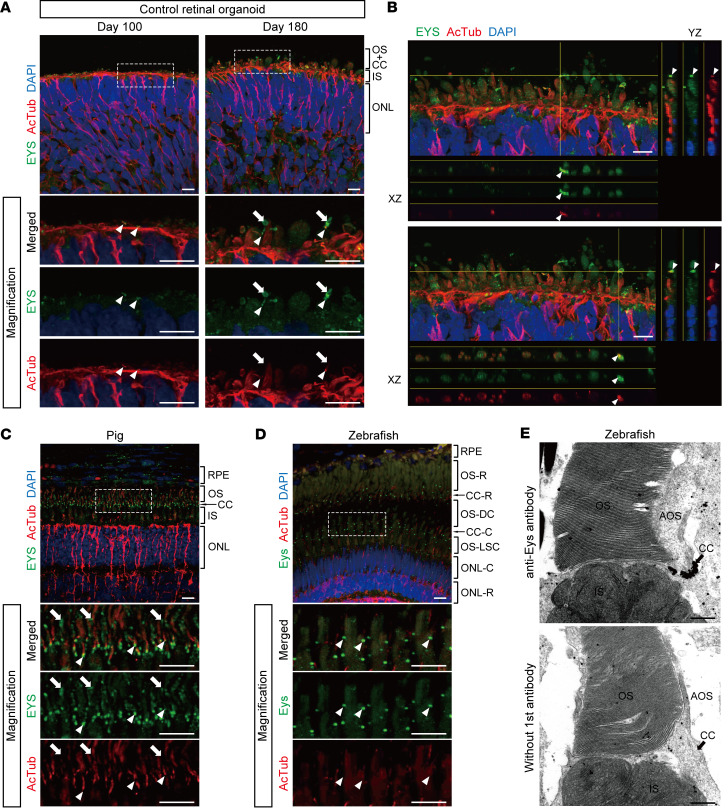
Figure 2. EYS localization in human retinal organoids, pig, and zebrafish.
(A) Representative immunofluorescence images of control retinal organoids on day 100 and day 180 stained for EYS and acetylated α-tubulin (AcTub). Lower panels are higher-magnification images of the dotted boxes in the upper panels. White arrowheads indicate the CC, and white arrows indicate the nascent OS. ONL, outer nuclear layer. Scale bars: 10 μm. (B) Two representative immunostaining images of control retinal organoids on day 180, using orthogonal projections. EYS immunoreactivity colocalized with AcTub (white arrowheads). Scale bars: 10 μm. (C) Representative immunohistochemistry images of EYS and AcTub in WT pig retina. Lower panels are higher-magnification images of the dotted box in the upper panel. White arrowheads indicate the CC, and white arrows indicate the OS. RPE, retinal pigment epithelium. Scale bars: 10 μm. (D) Representative immunohistochemistry images of Eys and AcTub in WT zebrafish retina. Lower panels are higher-magnification images of the dotted box in the upper panel. White arrowheads indicate the CC. CC-C, cone CC; CC-R, rod CC; ONL-C, cone ONL; ONL-R, rod ONL; OS-DC, double cone outer segment; OS-LSC, long single cone outer segment; OS-R, rod outer segment. Scale bars: 10 μm. (E) Representative immunoelectron microscopy images of WT zebrafish retina. Upper panel shows staining with anti-Eys antibody. Negative control without the primary antibody is shown in the lower panel. AOS, accessory outer segment. Scale bars: 500 nm.