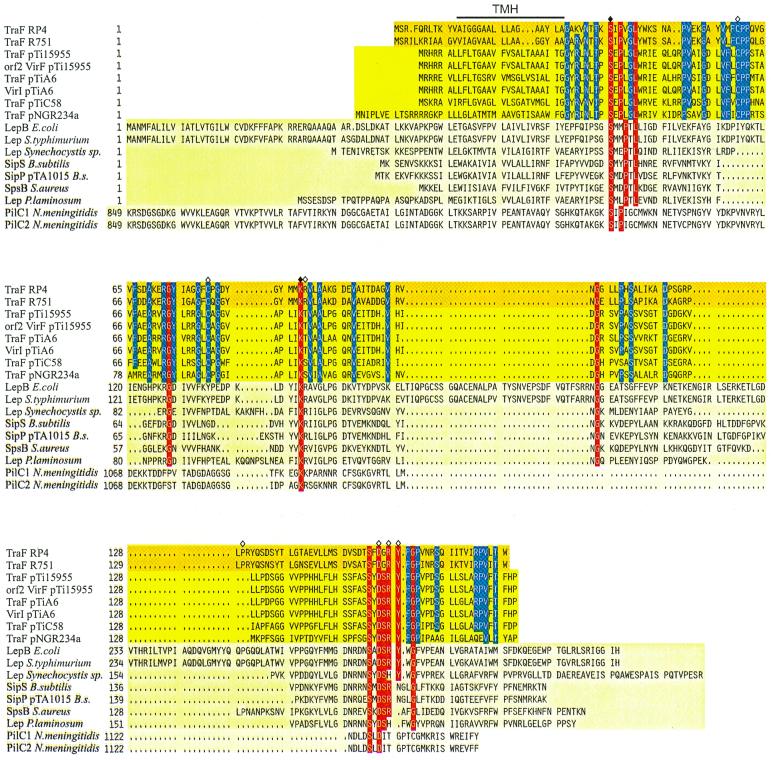
FIG. 2.
Sequence alignment of TraF-like proteins. Amino acid compositions of the different gene products are arranged in families; GenBank accession numbers are given in parentheses. Dark yellow background, bacterial conjugative plasmids' RP4 (L27758) and R751 (M94367) TraF. Yellow background, A. tumefaciens TraF homologues from pTi15955 (P15595), pTiA6 (U43674), pTiC58 (U40389), and putative pTi15955 protein Orf2 (S15913), pTiA6NC VirI (2773263), as well as Rhizobium Ti plasmid homologue pNGR234a TraF (P55417). Light yellow background, leader peptidases LepB of E. coli (K00426), Lep of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (X54933), Lep of Synechocystis sp. (PCC6803), SipS of B. subtilis (Z11847), SipP of B. subtilis plasmid pTA1015 (AAC44415), SpsB of Staphylococcus aureus (U65000), and Lep of Phormidium laminosum (S51921). Pale yellow background, N. meningitidis PilC1 and PilC2 (Y13020 and Y13021, respectively). Identical amino acid residues in at least 11 sequences are shown with a red background. The catalytically active residues shown for E. coli leader peptidase I are marked with a filled rhombus, the respective amino acids in RP4 TraF have been mutated, and further mutation sites in RP4 TraF are marked with an open rhombus, whereas the predicted transmembranal helix (TMH) for RP4/R751 TraF is indicated with a line above the alignment. Gaps introduced to maximize alignment are indicated by dots. To indicate the high conservation of TraF-like proteins in the uppermost two families, identical amino acid residues of these proteins are indicated by a blue background.