Figure 3. HC-HA/PTX3 inhibited heat hypersensitivity in wild-type (WT) mice after plantar-incision and attenuated DRG neuron activation.
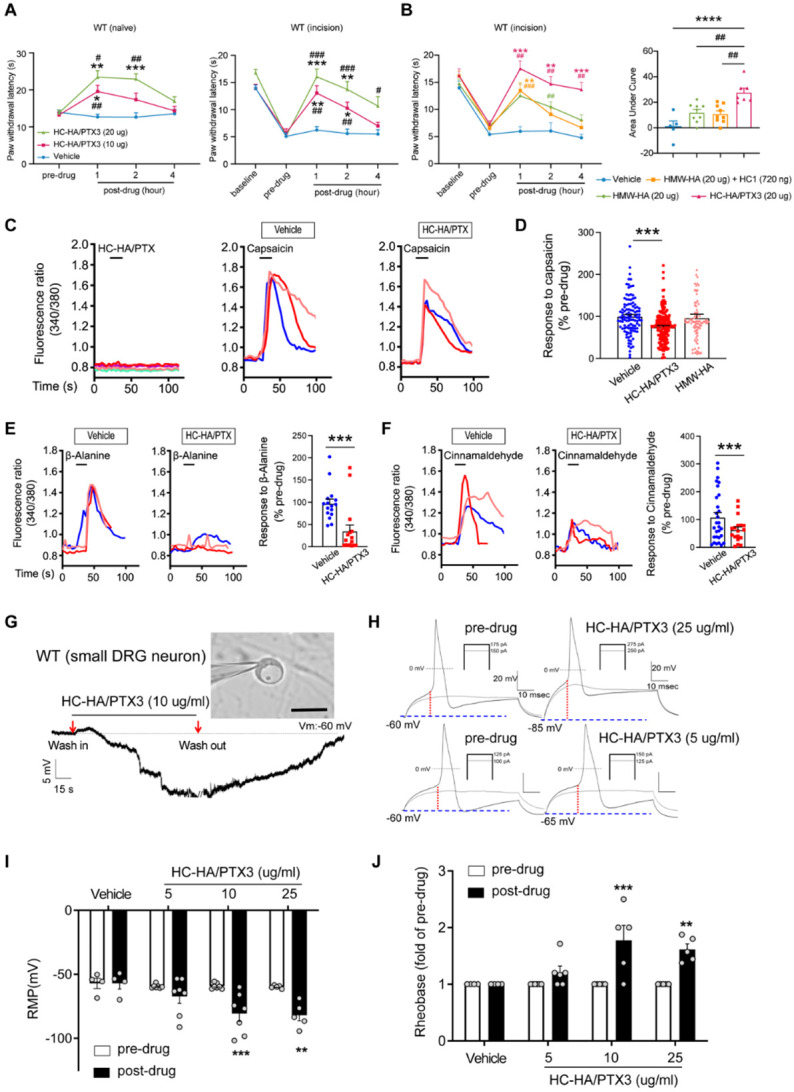
(A) Left: intra-paw injection of HC-HA/PTX3 (10 μg or 20 μg, 20 μL), but not vehicle (saline), increased paw withdrawal latency (PWL) to heat stimulation in naïve WT mice. N=8-11/group. Right: intra-paw injection of HC-HA/PTX3 (10 μg or 20 μg, 20 μL) dose-dependently attenuated the heat hypersensitivity during Days 2-4 after plantar-incision. N=9-16/group. (B) Right: intra-paw injection of HC-HA/PTX3 (20 μg, 20 μL) showed superior anti-hyperalgesic effect compared to HMW-HA ((20 μg, 20 μL)) alone and the mixture of HMW-HA (20 μg) and HC1 (720 ng) during days 2-4 after plantar-incision. Left: analyzing the Area Under the Curve (AUC) to assess the anti-hyperalgesic effect of each group. N=5-9/group. (C) HC-HA/PTX3 inhibited the calcium responses evoked by capsaicin (a TRPV1 agonist, 0.3 μM) in WT DRG neurons. HC-HA/PTX3 alone did not evoke [Ca2+]i elevation. Pre-treatment (20 min) of HC-HA/PTX3 (15 μg/mL, bath application) reduced capsaicin-evoked [Ca2+]i rising. (D) The quantification of [Ca2+]i rising evoked by capsaicin in DRG neurons pre-treated with the vehicle, HC-HA/PTX3 (15 μg/mL), or HMW-HA (15 μg/mL). N=109-170 neurons/group. (E) Left: Traces show that the β-alanine (a MrgprD agonist, 1 mM) evoked an increase in [Ca2+]i, which was also inhibited by HC-HA/PTX3. Right: The quantification of evoke [Ca2+]i rising by β-alanine. N=10-25 neurons/group. (F) Left: Traces show that cinnamaldehyde (a TRPA1 agonist, 1 mM) evoked an increase in [Ca2+]i, which was inhibited by HC-HA/PTX3. Right: The quantification of evoke [Ca2+]i rising by cinnamaldehyde. N=15-35 neurons/group. (G) An example trace of membrane potential (Vm) which changed from resting level (−60 mV) toward a more hyperpolarized state after HC-HA/PTX3 (10 μg/mL) in a small DRG neuron (insert, scale bar: 25 μm). Vm returned to pre-drug level after washout. DRG neurons were categorized according to cell body diameter as <20 μm (small), 20–30 μm (medium), and >30 μm (large). (H) Example traces of action potentials (APs) evoked by injection of current in small DRG neurons 5 min after bath application of vehicle or HC-HA/PTX3 (5, 25 μg/mL). (I) HC-HA/PTX3 concentration-dependently altered the intrinsic membrane properties of small DRG neurons. Quantification of the resting membrane potential (RMP) before and at 5 min after bath application of vehicle or HC-HA/PTX3 (5, 10, 25 μg/mL). N=4-7/group. (J) Quantification of rheobase in small DRG neurons at 5 min after vehicle or HC-HA/PTX3. The rheobase after drug was normalized to pre-drug value. N=5-7/group. Data are mean ± SEM. (A, B: right) Two-way mixed model ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. *P< 0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 versus vehicle; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 versus pre-drug. (B: left, C) One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. ***P<0.001 versus vehicle; ##P<0.01 versus other groups. (E, F) Paired t-test. ***P<0.001 versus vehicle. (I, J) Two-way mixed model ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 versus pre-drug.
