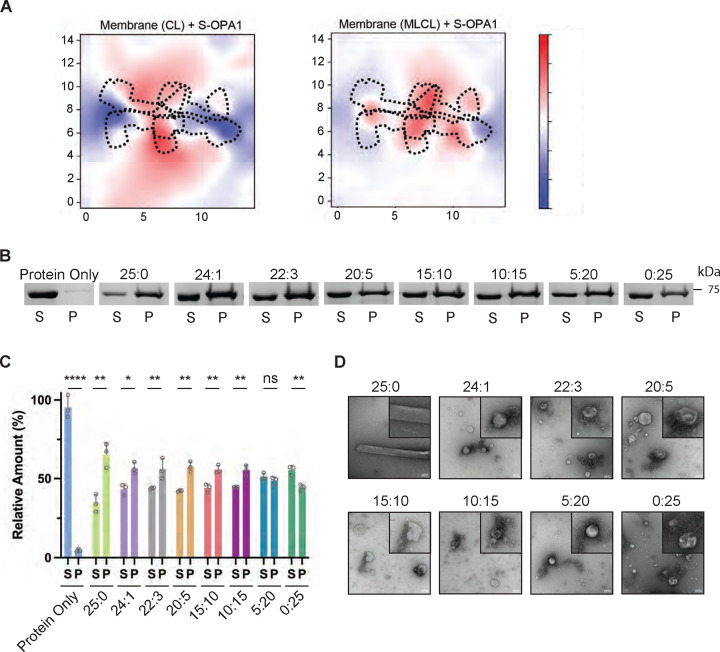
Figure 4. S-OPA1 interactions with MLCL-containing membranes.
(A) Membrane deformation calculations are shown for one of the three independent replicas using S-OPA1 tetramer 1 and model membranes containing either 20% CL (left) or 20% MLCL (right). Red and blue colors indicate membrane pulling and pushing in the direction of z, respectively. The membrane deformation activity of tetramer 1, particularly its ability to push down on the sides, is reduced in the presence of MLCL. (B) The co-sedimentation assays with S-OPA1 WT and liposomes containing CL and increasing molar ratios of MLCL. Supernatant and pellet samples from the co-sedimentation assays were harvested after centrifugation and analyzed by SDS-PAGE. (C) The assays were performed in triplicates and gel images were quantified by ImageJ. An unpaired two-tailed student T test was used for statistical analysis. The asterisk(s) above the bars indicate the following: P<0.0001 (****), P<0.001 to P>0.0001(***), P<0.005 to P>0.001 (**), P<0.05 to P>0.005(*), and P>0.05 (not significant, ns). (D) Representative negative-stain TEM images of reconstitution assays in the presence of CL and MLCL containing liposomes. Increasing molar ratios of MLCL impairs the membrane remodeling activity of S-OPA1. Scale bars are 100 nm.