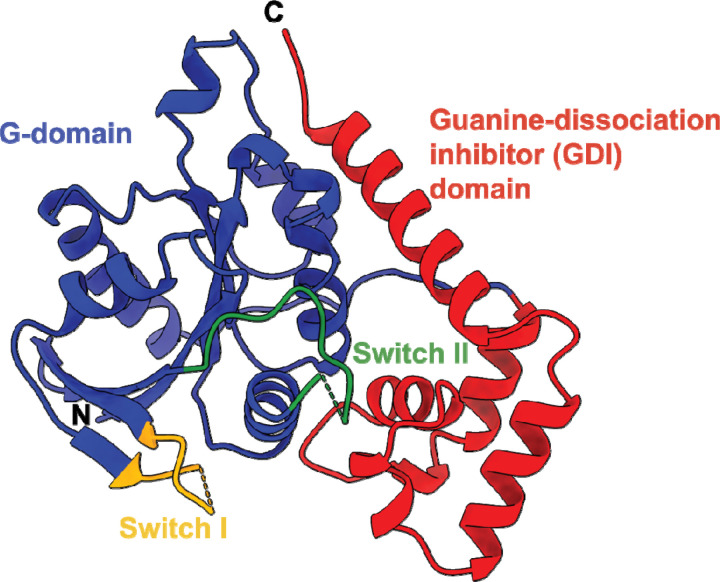
Fig. 2.
X-ray crystal structure of the SUMO-cleaved Vibrio cholerae NFeoB NTPase domain in the apo state (PDB ID 9BA6). The overall structure of the VcNFeoB has a typical NFeoB fold and comprises two major domains: the guanine-dissociation inhibitor (GDI) domain (labeled in red) that regulates GDP release and connects to the transmembrane region, and the G-protein domain (labeled in blue) that binds and catalyzes nucleotide hydrolysis. Within the G-protein domain are two key switch regions (Switch I and Switch II, labeled yellow and green respectively) that regulate nucleotide hydrolysis and transmit information to the GDI domain. In the absence of nucleotide, Switch I is mostly disordered, while Switch II is mostly ordered. ‘N’ and ‘C’ represent the N- and C-termini in the structure, respectively.