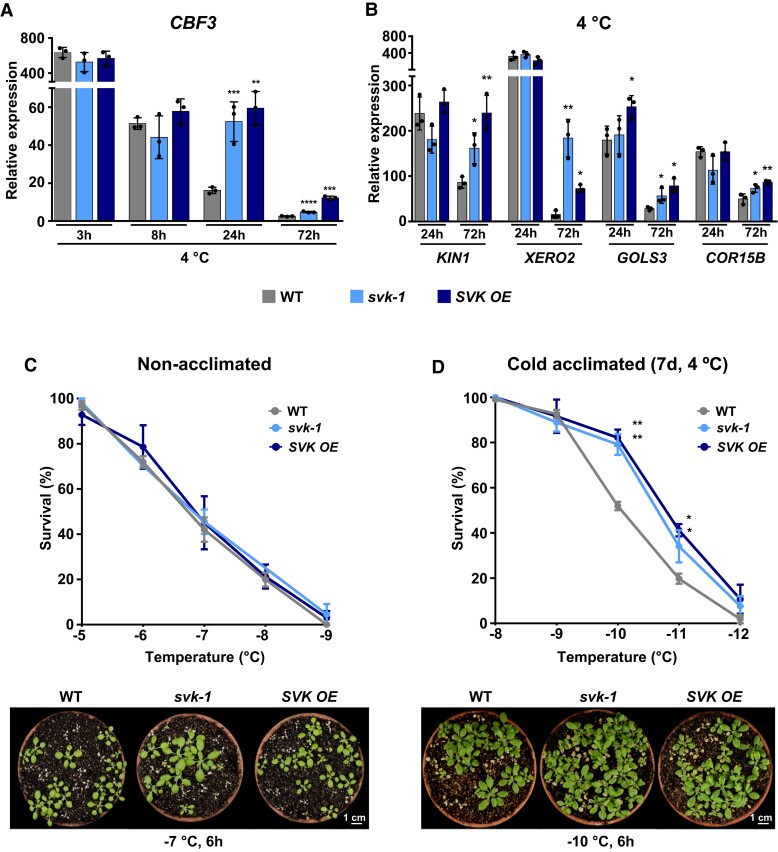
Figure 2.
SVALKA regulates the cold acclimation response by mediating the decline of CBF3 induction. A and B) Expression analysis of CBF3 (A) and CBF3 target genes KIN1, XERO2, GOLS2, and COR15B (B) in 2-wk-old WT, svk-1 and SVK OE plants exposed to 4 °C for the indicated additional hours (3, 8, 24, or 72 h). In each case, transcript levels, determined by RT-qPCR, are represented as relative to the values of the WT plants grown under control conditions. Primer set 5 in Fig. 1A was used for expression analyses of CBF3. C and D) Freezing tolerance of nonacclimated (C) and cold acclimated 7 d at 4 °C (D) 2-wk-old WT, svk-1 and SVK OE plants exposed to the indicated freezing temperatures for 6 h. Tolerance was estimated as the percentage of plants surviving each specific temperature after 1 wk of recovery under control conditions. Lower panels show the freezing tolerance of representative nonacclimated and cold acclimated plants. Images were digitally extracted for comparison. In all panels, asterisks indicate significant differences (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001) between svk-1 and SVK OE mutants and the corresponding WT plants, as determined by one-sided t test. Data represent the mean of three independent experiments and error bars show the standard deviation.