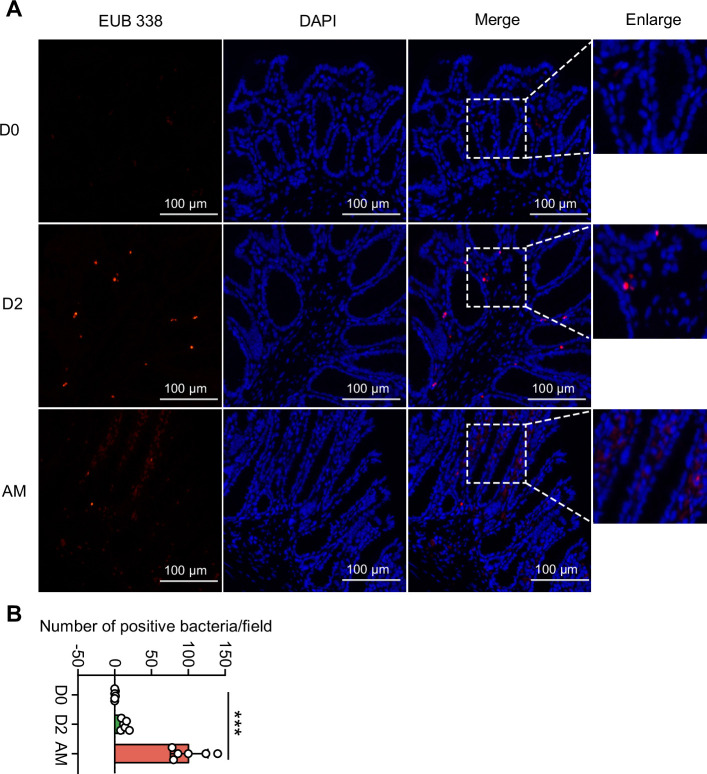
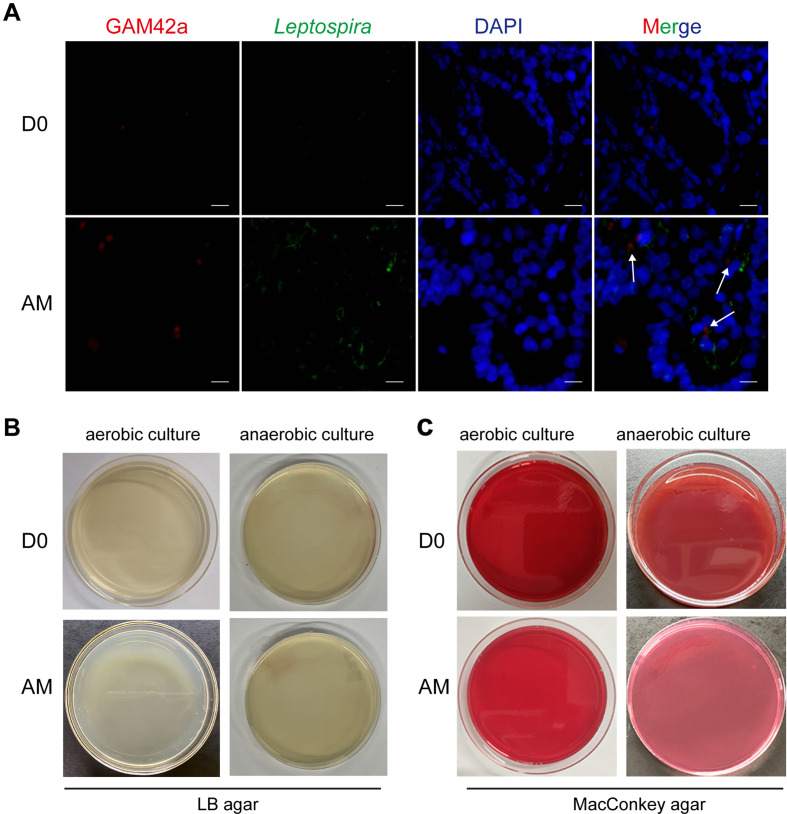
Figure 4. Translocated microbiota in the intestinal epithelium following L. interrogans infection.
Six-week-old female hamsters were injected intraperitoneally with 107 leptospires. Hamsters were euthanized at 0 d, 2 d, and AM post infection (p.i.). Colons were collected aseptically. The intestinal contents were excluded from the intestine with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and a segment of the colon was fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde solution overnight and analyzed by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) with an EUB 338 probe (red). (A) The results are representative photographs of three groups. Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) Number of positive bacteria per field in the three groups. n = 6 per group. D0, uninfected hamster; AM, articulo mortis. Each infection experiment was repeated three times. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM and analyzed by using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test. ***p<0.001.