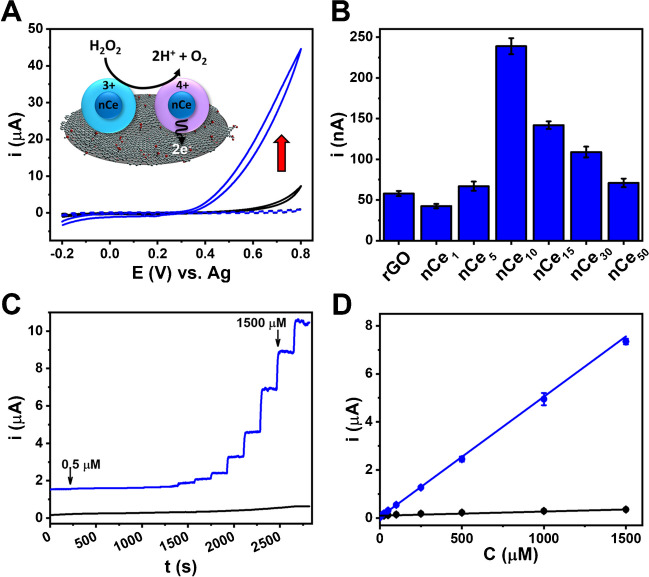
Fig. 4.
A Cyclic voltammograms for rGO (black line) and rGO-nCe10 (blue line) sensors performed in 10 mM H2O2 in PB, and cyclic voltammogram of rGO-nCe sensor acquired in PB only (dashed blue line); scan rate 25 mV s−1. The inset graphically resumes the catalytic mechanism of nCe toward hydrogen peroxide. B Amperometric currents obtained in presence of 50 µM H2O2 for rGO and rGO-nCe1−15 sensors E = + 0.4 V vs. Ag. C Amperometry measurements carried out at +0.4 V increasing the amount of H2O2; the arrow indicates the linear range (0.5 to 1500 μM) for the rGO-nCe10. D Linearly fitted data for the rGO (black line; L.R. 25–1500 μM, linear fit eq: y = 0.173 [± 5.9 × 10−3] x + 97.222 [± 1.181]; R2 = 0.9943) and rGO-nCe10 (blue line; L.R. 0.5–1500 μM, linear fit eq: y = 5.014 [± 0.088] x + 38.760 [± 3.315], R2 = 0.9985) sensor. The relative measurement performed in the buffer was subtracted from each signal