FIGURE 2.
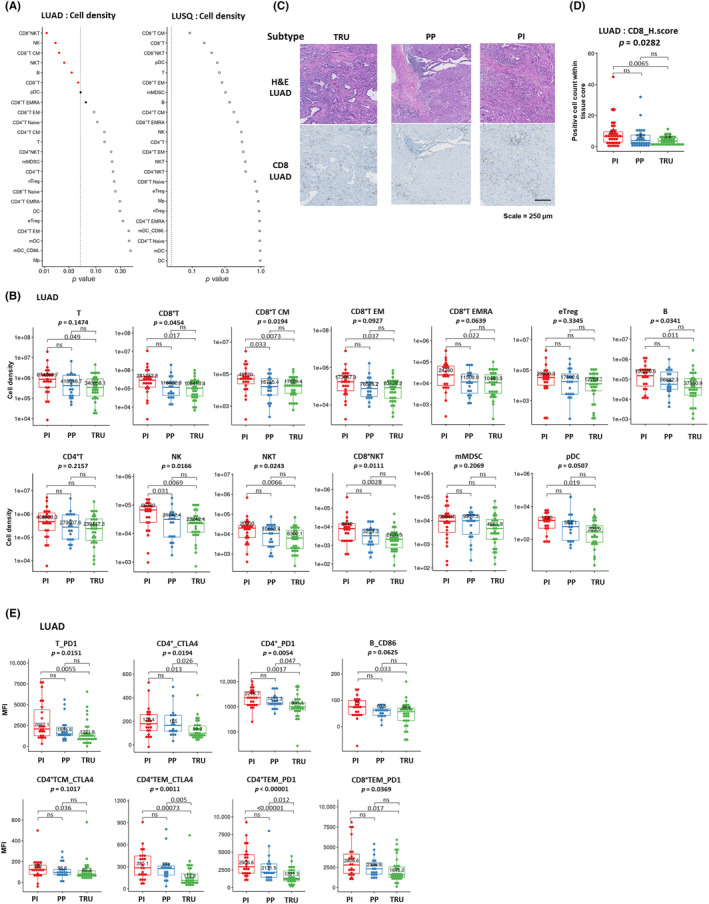
Immune profile of lung cancer molecular subtypes. (A) Relationships between cell density for each immune cell fraction infiltrated in tumors and molecular subtypes of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD; left) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSQ; right). (B) Cell densities of immune cell fractions in each LUAD molecular subtype were analyzed using flow cytometry (FCM) (proximal inflammatory [PI], n = 23; proximal proliferative [PP], n = 19; terminal respiratory unit [TRU], n = 30). (C) H&E and immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for CD8 in a representative case of each LUAD molecular subtype (PI, n = 35; PP, n = 34; TRU, n = 37). The positivity of each marker is given as the number of total positive cells within each tissue core. (D) Immune‐cell count by IHC staining in lung cancer tissues in each LUAD molecular subtype. The positivity of each marker is given as the number of total positive cells within each tissue core. (E) Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of functional molecules in immune cell fractions according to LUAD molecular subtype by FCM. CM, central memory; DC, dendritic cell; EM, effector memory; EMRA, effector memory cells re‐expressing CD45RA; mMDSC, monocytic myeloid‐derived suppressor cell, NK, natural killer; ns, not significant.
