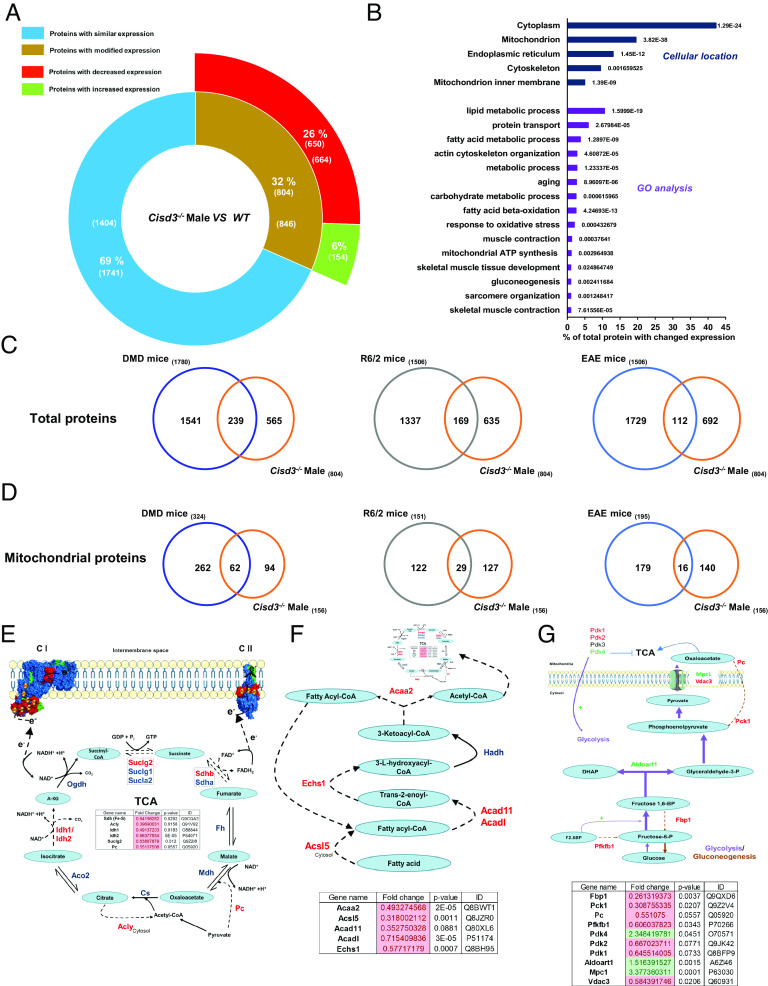
Fig. 3.
Proteomics analysis of skeletal muscles from wild-type and Cisd3−/− mice. (A) A diagram showing the number of proteins altered in Cisd3−/− mice compared to the wild type (WT) in quadricep muscle tissues of 44-wk-old mice. (B) Subcellular localization and gene ontology (GO) annotation of proteins altered in Cisd3−/− mice compared to WT. (C) Venn diagrams showing the overlap between proteins altered in Cisd3−/− mice and proteins altered in mice model systems for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD), Huntington Disease (HD; R6/2), and Multiple Sclerosis (MS; EAE). (D) Same as in (C) but for mitochondrial proteins. (E–G) Changes in protein abundance in Cisd3−/− mice are shown for the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA; E), fatty acid oxidation (F), and glycolysis/gluconeogenesis (G) pathways. Results are shown for male mice and presented as mean ± SD of three different animals from each group (WT and Cisd3−/− mice). Two-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey test was used to calculate statistical significance. Abbreviations: CISD, CDGSH Iron Sulfur Domain; DMD, Duchenne muscular dystrophy; EAE, experimental allergic encephalomyelitis; HD, Huntington disease; GO, gene ontology; GO, gene ontology; KO, knock out; MS, multiple sclerosis; WT, wild type; Cs, citrate synthase; Acly, ATP-citrate synthase; Aco2, Aconitase 2; Idh, Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NADP]; Ogdh, Oxoglutarate Dehydrogenase; Suclg, Succinate--CoA ligase; Pc, pyruvate carboxylase; Sdh, Succinate dehydrogenase [ubiquinone]; Fh, Fumarate hydratase; Mdh, Malate dehydrogenase; A-KG, α-Ketoglutarate; Acaa2, 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase; Acsl5, Long-chain-fatty-acid—CoA ligase 5; Acad11, Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family member 11; Acadl, Long-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; Echs1, Enoyl-CoA hydratase; Fbp1, Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1; Pck, Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; Pfkfb1, 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase 1; Pdk, Pyruvate dehydrogenase (acetyl-transferring)] kinase; Aldoart1, Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase; Mpc, Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier; Vdac3, Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 3, F2.6BP, Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate; DHAP, Dihydroxyacetone phosphate.