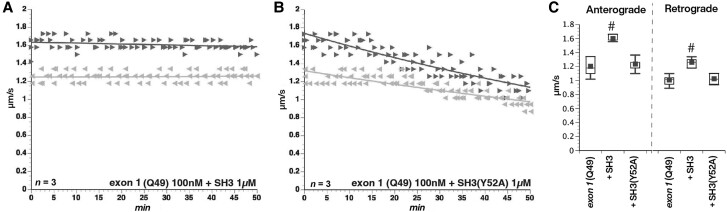
Figure 8.
Toxic effects of mHTT on fast axonal transport involve binding to SH3 domain-containing proteins. Proline-rich domains are implicated in a variety of protein–protein interaction domains. (A) SH3-binding domains are a common motif with a characteristic PXXP conserved sequence. The PRD contains multiple PXXP motifs, so we co-perfused mHTT exon 1 (Q49) (100 nM) with a peptide containing an SH3 motif at 1 µM. Excess SH3 peptide prevents mHTT exon 1 (Q49) effects on fast axonal transport. (B) In contrast, a mutant SH3 domain that no longer binds PXXP motifs (SH3-Y52A) at 1 µM fails to protect fast axonal transport. (C) Preincubation with a recombinant peptide encoding an SH3 motif blocked effects of mHTT exon 1 (Q49) on both anterograde and retrograde transport rates (P < 0.0001), whereas a mutant SH3 peptide unable to bind SH3-binding motifs (Y52A) did not (P = 0.41 for anterograde rates; P = 0.1964 for retrograde rates). #P < 0.0001.