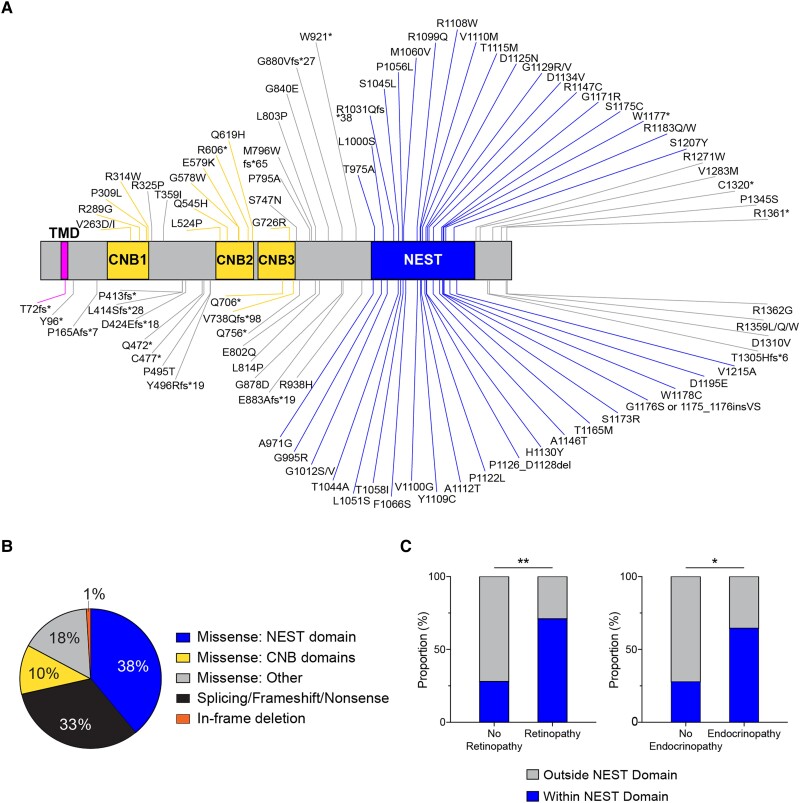
Figure 1.
Summary of systematic evidence-based review of patients with PNPLA6 variants. (A) Schematic of the protein domain architecture and the location of 93 PNPLA6 missense, truncating, nonsense and in-frame variants (excluding 11 splice variants, one duplication and one deletion) known since May 2023 (NCBI reference NP_001159583.1). Neuropathy target esterase (NTE) contains a single pass transmembrane domain (aa60-80), three cyclic nucleotide binding (CNB) domains, and a NTE-esterase (NEST) domain. Figure generated using IBS Cuckoo illustration software.48 (B) Frequency distribution of variants based on their locations on the protein and variant type. Missense: NEST domain, n = 40; splicing/frameshift/nonsense, n = 35; Missense: CNB domains, n = 11; Missense: Other, n = 19; in-frame deletion: n = 1. (C) Missense variants categorized within the NEST domain (aa964–1269) and outside the nest domain (aa1–964, aa1270–1375) were grouped by their association with/without retinopathy and endocrinopathy. (C) Used a Fisher’s exact test with α = 0.05. Additional genotypic information can be found in the Supplementary material, ‘Supporting data values’ file.