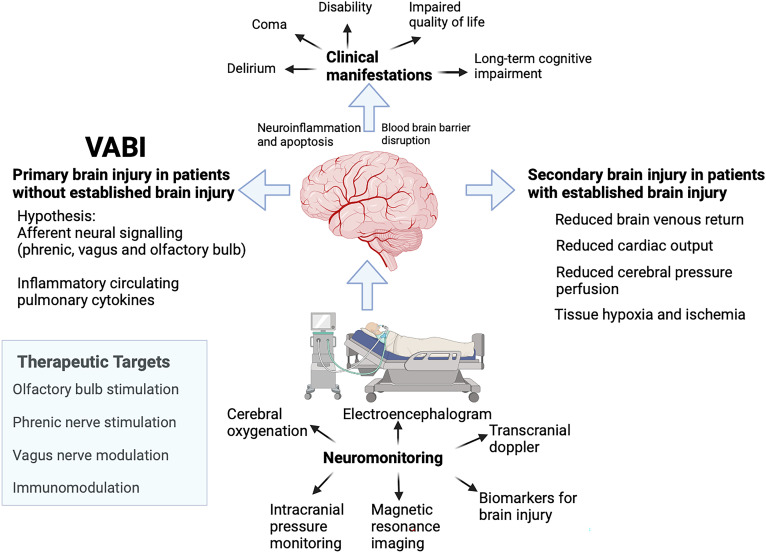
Figure 1.
Brain injury from mechanical ventilation. Mechanical ventilation may cause brain injury secondarily in patients with established acute brain injury by potentiating ischemia, particularly when cerebral autoregulation is impaired and intracranial pressure is increased. Mechanical ventilation may also cause primary brain injury in the absence of established brain injury by various possible mechanisms. In both forms of injury, neuromonitoring techniques might be useful to detect and monitor such injury. Possible therapeutic targets could be phrenic nerve stimulation, olfactory bulb stimulation, and vagus and immune modulation. VABI = ventilator-associated brain injury. Figure created with BioRender.