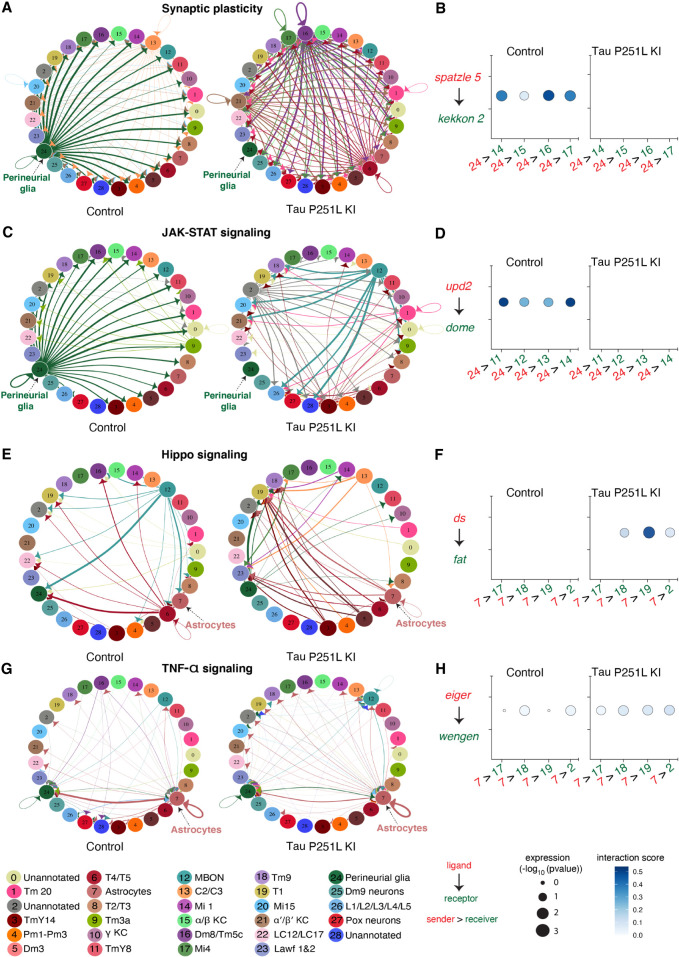
Figure 6.
Cell–cell communication analysis predicts altered signaling in Tau P251L knock-in brains compared with controls. (A) Altered ligand and receptor expression predicts regulation of synaptic plasticity signaling mainly via perineurial glial cells in control brains. (B) Signaling from perineurial glia is significantly reduced in Tau P251L knock-in brains, as predicted by levels of spaetzle ligand and kekkon receptor. (C,D) JAK-STAT signaling, as predicted by expression of the upd2 ligand and dome receptor, mediated by perineurial glia in control brains (C), is substantially reduced in brains from Tau P251L knock-in animals (D). (E,F) Hippo signaling, indicated by expression of ds ligand and fat receptor, is up-regulated in astrocytes of flies expressing P251L mutant Tau compared with controls. (G,H) Predicted TNF-α signaling from ligand eiger to receptor wengen is increased in astrocytes of Tau P251L knock-in flies. In panels B,D,F,H, the interactions from and to the specified cell types are indicated on the x-axis, the size of the circle indicates the P-value, and the intensity of the blue color illustrates the interaction score as defined in the figure label below the panels.