Fig. 2.
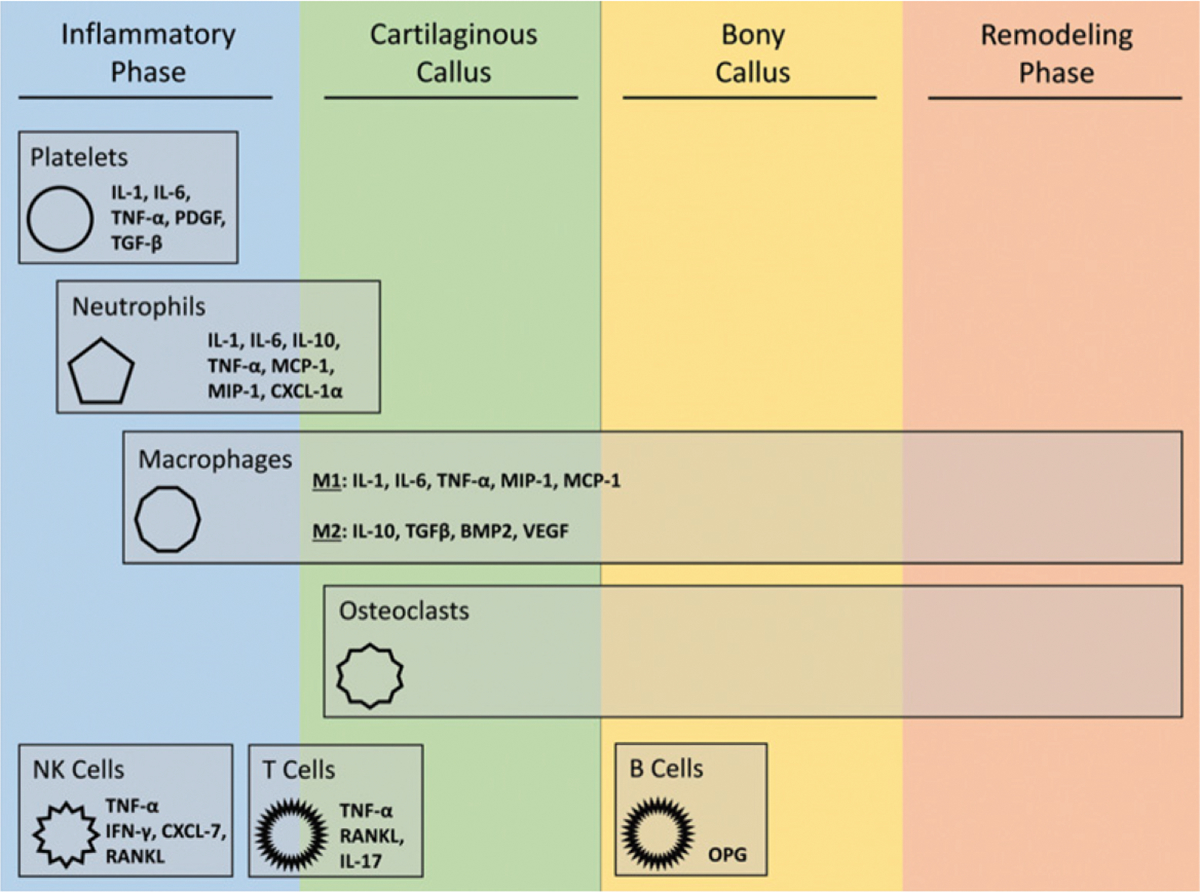
The role of immune cells during fracture repair14. Bone fracture-healing can be viewed as a 4-stage process. Immune cells play important roles throughout this process; however, a majority of their activity occurs during the early stages of fracture-healing. IL = interleukin, TNF-α = tumor necrosis factor-alpha, PDGF = platelet-derived growth factor, TGF-β = transforming growth factor-beta, MCP1 = monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, MIP-1 = macrophage inflammatory protein-1, CXCL = C-terminal crosslinking telopeptide of type-I collagen, BMP2 = bone morphogenetic protein-2, VEGF = vascular endothelial growth factor, NK = natural killer, IFN-γ = interferon gamma, RANKL = receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand, and OPG = osteo-protegerin. (Reproduced from: Baht GS, Vi L, Alman BA. The role of the immune cells in fracture healing. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2018 Apr;16[2]:138–45, under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.)
