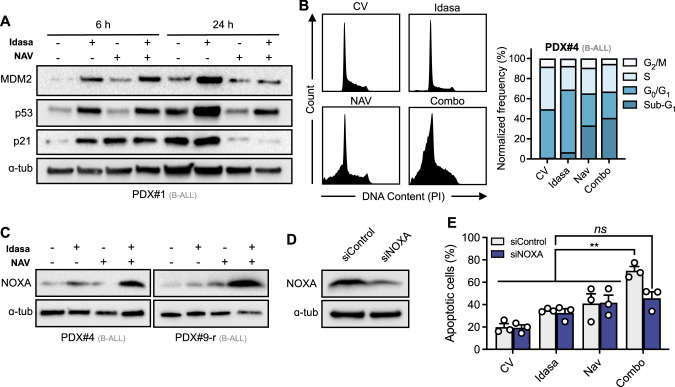
Fig. 5. Combination of idasanutlin and navitoclax prioritizes cell death over cell cycle arrest via a mechanism involving pro-apoptotic protein NOXA.
A Representative immunoblots showing MDM2, p53, and p21 expression in B-ALL PDX#1 following exposure to respective IC50 concentrations of idasanutlin, navitoclax, or their combination for 6 h or 24 h (N = 1). B Cell cycle analysis of B-ALL PDX#4 exposed to respective IC50 concentrations of idasanutlin, navitoclax, or their combination for 24 h. N = 1 independent experiment. C Immunoblots showing protein expression levels of NOXA in PDX samples following exposure to respective IC50 concentrations of idasanutlin, navitoclax, or their combination for 24 h. Data show representative data of N = 3 independent PDX samples. D Immunoblot showing representative protein expression of NOXA/PMAIP1 following siRNA-mediated (300 nM) knockdown of NOXA/PMAIP1 or a non-targeted control in the NALM6 cell line. N = 3 independent experiments. E Apoptotic cells were quantified by annexin-V flow cytometry in NALM6 cells transfected with non-targeting control siRNA or PMAIP1/NOXA siRNA, following exposure to respective IC50 concentrations of idasanutlin, navitoclax, or their combination for 48 h. Error bars show mean ± s.d of three independent experiments. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Tukey posttest for multiple comparisons. ns=not significant, **p-value < 0.01. In (A, C, D), ɑ-tubulin served as the loading control.