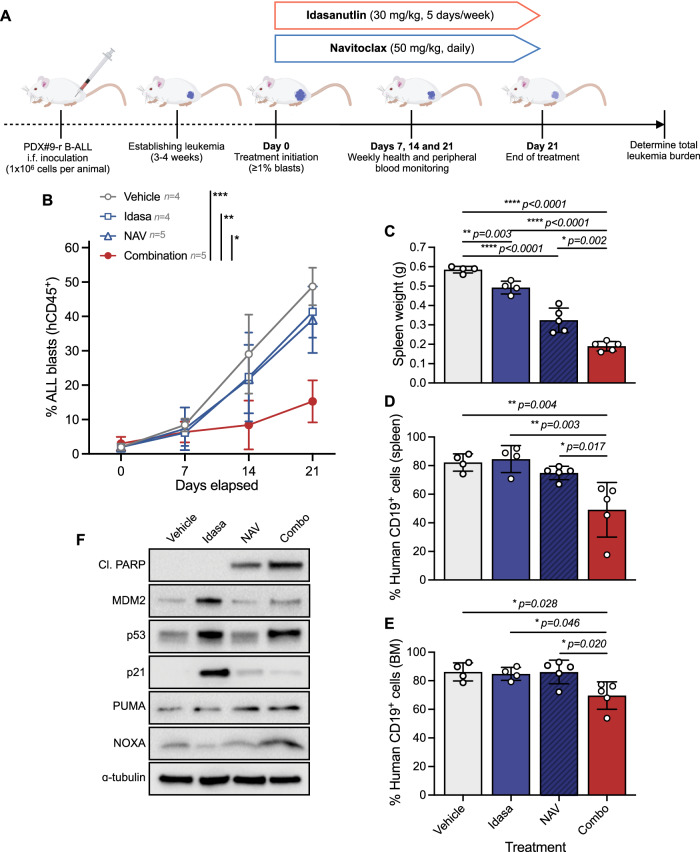
Fig. 6. Combination of idasanutlin and navitoclax synergistically inhibits in vivo growth in a high-risk relapsed ALL xenograft model.
A Schematic of experimental approach. B NSG mouse recipients received 1 × 106 viable B-ALL PDX#9-r cells intrafemorally and when human ALL blasts in the peripheral blood reached ≥ 1%, mice were randomized to receive idasanutlin (30 mg/kg) once daily five days per week, navitoclax (50 mg/kg) once daily, and their combination for 21 days by oral gavage. C Spleen weights from recipients following treatment with idasanutlin (30 mg/kg) once daily five days per week, navitoclax (50 mg/kg) once daily, and their combination for 21 days by oral gavage. Mice were euthanized within 24 h of their final dose. D Quantification of human CD19 + B-ALL cells by flow cytometry analysis of splenocytes from engrafted mice. E Quantification of hCD19+ B-ALL cells by flow cytometry analysis of bone marrow from engrafted mice. F Steady-state pharmacodynamic analyses of spleen blasts derived from PDX#9-r engrafted mice treated with each treatment arm for three consecutive days (n = 3 per group). Immunoblots show induction of cleaved PARP (Asp214), on-target p53 pathway signaling, and enhanced NOXA. ɑ-tubulin served as the loading control. In (B–E), treatment groups were compared by two-way ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc test and error bars indicate mean±s.d.