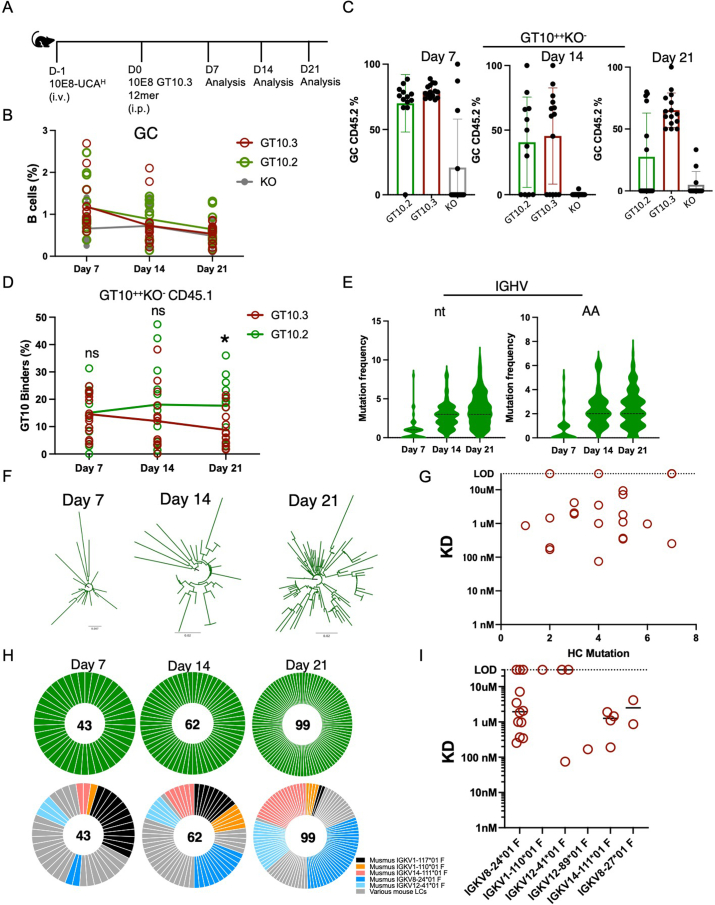
Extended Data Fig. 9. Higher affinity 10E8-GT10.3 improves GC sustenance of 10E8 B cells, related to Fig. 6.
a, Schematic of CD45.1+ mice adoptively transferred to establish a frequency of 1:104 CD45.2+10E8-UCAH B cells and then immunized with either 5 μg of 10E8-GT10.3 12mer, 10E8-GT10.2 12mer, or a control KO immunogen with alhydrogel, as in Fig. 6c. b, Quantification of percentage of GC B cells post immunization with 10E8-GT10.3 12mer, 10E8-GT10.2 12mer, or 10E8-GT9-KO 12mer. Data are pooled from two independent experiments (n = 5–8) with lines marking the respective means. c, Quantification of epitope specific (GT10++KO−) CD45.2+10E8-UCAH B cells in GC in mice immunized with 10E8-GT10.2 12mer or 10E8-GT10.3 12mer at different time points, as in a. Error bars indicate mean ± SD from mice in each group (n = 5–8). Data are pooled from two independent experiments. d, Quantification of epitope specific CD45.1+ cells in GC in mice immunized as in a. Data are pooled from two independent experiments. *p =0.0137(unpaired t test, two tailed); ns, not significant. N = 5–8 mice in each group; lines mark means. e, Mutations in IGHV of GT10-specific 10E8-UCAH B cells 7, 14, and 21 DPI. (Left) Nucleotide (nt); (right) amino acid (aa). The black dashed line indicates the median number of mutations. f, Diversification of IGHV sequences from 10E8-UCAH B cells isolated at 7, 14, and 21 DPI with 10E8-GT10.3 12mer as in e. g, Graph comparing the number of mutations in heavy chain of 10E8-UCA cells (x-axis) against their affinity (y-axis) (shown in Fig. 6e) 21 DPI with 10E8-GT10.3 12mer. h, HCs (top) LCs (bottom) sequenced from GT10-specific 10E8-UCAH B cells 7, 14, and 21 DPI by 10E8-GT10.3 and alhydrogel, as in a. Numbers inside pie shows the number of cells sequenced. i, Graph showing the affinities of the 10E8-UCAH 21 DPI as per in Fig. 6e with the associated mouse light chains.