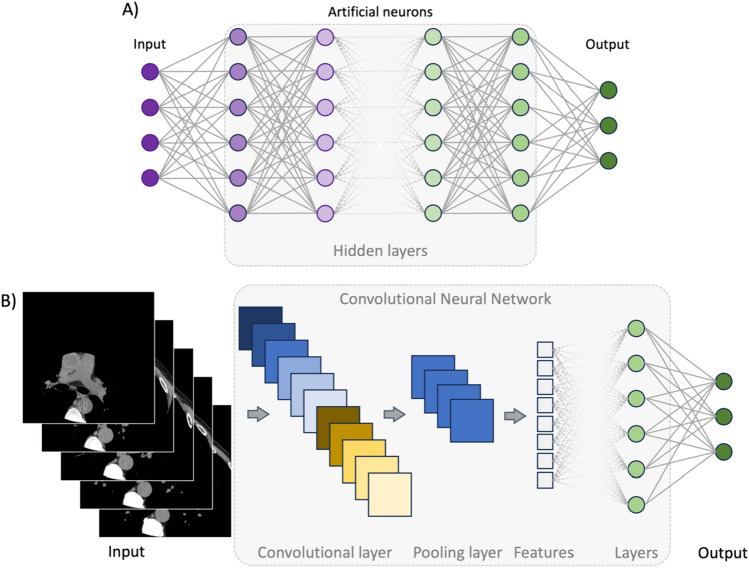
Fig. 1.
Deep-learning and convolutional neural network algorithm architecture. A Deep learning (DL) relies on multiple hidden layers of artificial neural networks (ANN), hence the name "deep". These layers are usually defined as "hidden" because they do not belong either to the input or output layer. The number of hidden layers determines the depth of a model. Their role is to capture patterns and features, transforming input data into other data forms usable by the subsequent layer of neurons. Indeed, each neuron contained in these layers relates to the formers. Information flows from layer to layer, moving from input to output, progressively increasing its complexity and abstractedness. B Convolutional neural networks (CNN) are the most common DL architecture used in image analysis. This architecture has two major components: convolutional and pooling layers. The former is the core building of a CNN and works by applying filters to the input data, generating an activation map. Pooling layers combine the outputs of the convolutional step, reducing the number of features extracted. These steps can be repeated multiple times. Usually, the last step is allocated to layers of artificial neural networks, which in turn generates the output. ANN artificial neural network, CNN Convolutional neural network, DL deep learning