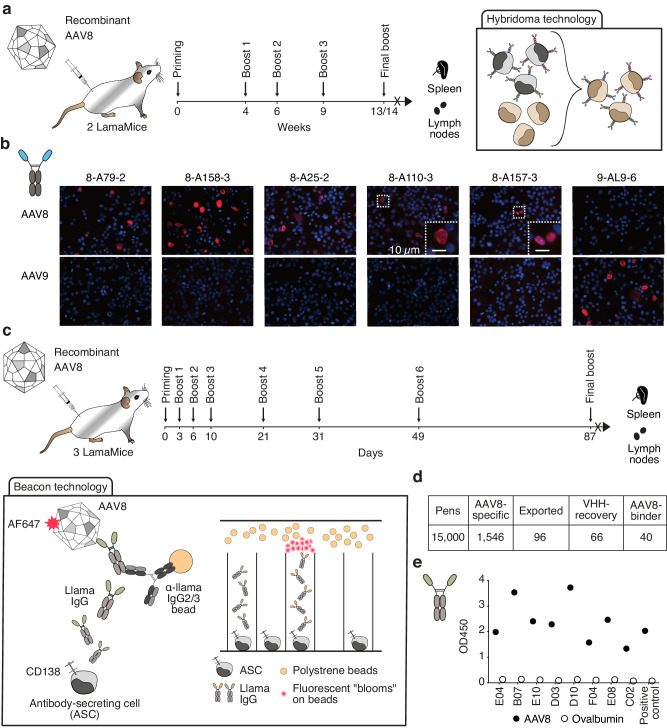
Fig. 3. Discovery of AAV-specific nanobodies from immunized LamaMice using classic hybridoma or single B cell screening technologies.
a LamaMice were immunized with AAV8 as indicated. Three days after the final boost, spleen and lymph node cells were fused with Sp2/0 mouse myeloma cells and cultured on 96-well plates in HAT-selection medium. Supernatants of hybridoma clones were screened by ELISA for reactivity with AAV8. Positive hybridomas were subcloned by limiting dilution. b The VHH-encoding region of positive clones was PCR-amplified, sequenced, and cloned into a mammalian expression vector upstream of the hinge, CH2 and CH3 of rabbit IgG. VHH-rabbit IgG hcAbs were produced in transiently transfected HEK-6E cells and cell supernatants were analyzed for reactivity with HEKAAV cells producing AAV by immunofluorescence microscopy. Bound hcAbs were detected with PE-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG. c, d LamaMice were immunized with AAV8 as indicated. Four days after the final boost, antibody-secreting cells (ASC) were sorted from spleen and lymph node cells using anti-CD138-coated beads, and cells were loaded into individual pens on a Berkley Lights Beacon® chip. Llama IgG heavy chain antibodies (hcAbs) captured on beads were detected with AF647-conjugated AAV8. Cells yielding an AAV8-specific signal were exported onto a 96-well plate and subjected to cDNA synthesis. e PCR-amplicons obtained with a VHH-specific primer pair were sequenced and cloned into a mammalian expression vector. VHHs were re-expressed as recombinant llama hcAbs and tested for specific binding to AAV8 by ELISA. Bound hcAbs were detected with PO-conjugated anti-llama IgG.