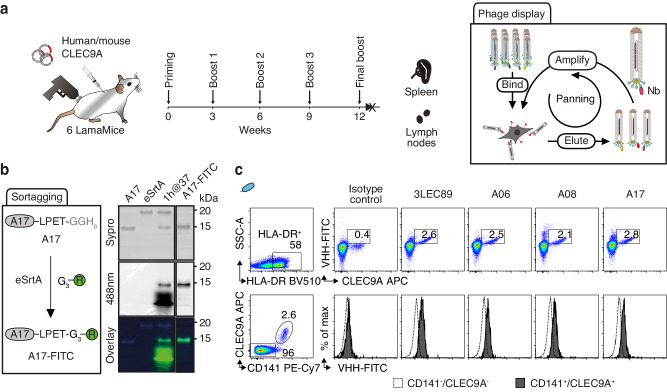
Fig. 6. Discovery of CLEC9A-specific nanobodies from cDNA-immunized LamaMice using phage display technology.
a LamaMice were immunized with a cDNA expression vector encoding human CLEC9A using a gene gun. Three days after the final boost, the VHH-repertoire was PCR-amplified from cDNA prepared from spleen and lymph nodes and cloned into the pHEN2 phagemid vector as in Fig. 5. Phage display libraries were panned on cells expressing cell surface CLEC9A. b The VHH-encoding region of enriched phages was subcloned upstream of the coding sequence for a sortase tag and VHHs were fused to a FITC-conjugated peptide using sortase (eSrtA). Unreacted product and sortase were removed with Ni-NTA resin and excess nucleophile was removed by spin filtration. In-gel Sypro (protein) and FITC fluorescence of reaction products were analyzed via SDS-PAGE. c Binding of FITC-conjugated VHHs to CLEC9A-expressing human peripheral blood cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. Gating was performed on MHCII HLA-DR+ cells (upper panels). Cells were counterstained with commercial CLEC9A-specific and CD141-specific mAbs. Gating was performed on HLA-DR+ cells that were either CD141+ or CD141- (lower panels).