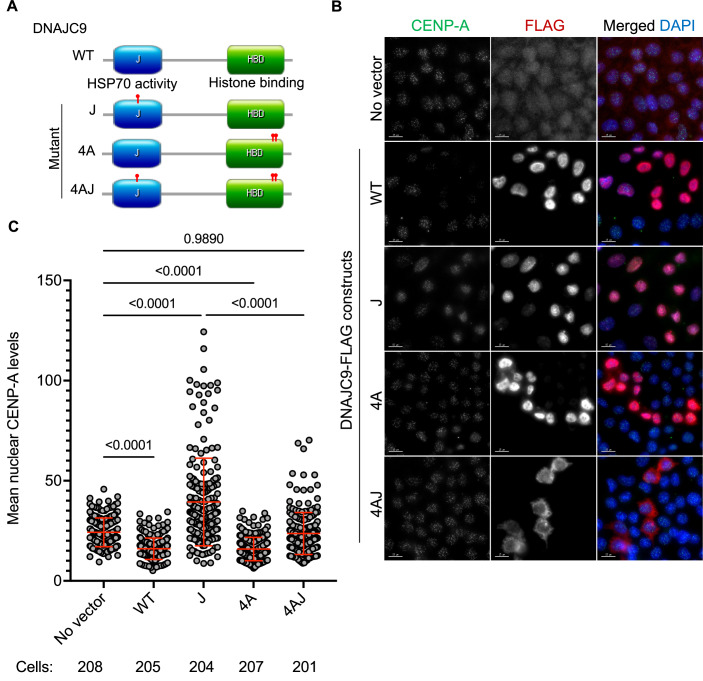
Figure 7. Catalytically inactive DNAJC9 promotes CENP-A mislocalization in a H3-dependent manner.
(A) Schematic representing the organization of domains in DNAJC9 and sites of mutations in the J domain and/or histone-binding domain (HBD) marked with red pointers. WT wild-type DNAJC9, J mutant DNAJC9 with mutation in J domain, 4A mutant DNAJC9 with mutations in histone-binding domain, 4AJ DNAJC9 with mutations in histone binding and J domains. (B) Increased nuclear CENP-A levels are observed in cells expressing catalytically inactive J mutant. Immunofluorescence images showing nuclear CENP-A levels in HeLa YFP-CENP-ALow cells from three independent experiments, post transient transfection with the indicated constructs as described in (A), for 72 h. Scale bar: 15 µm. (C) Scatter plot showing nuclear CENP-A intensities for conditions as described in (A). The total number of cells analyzed per condition from three biological replicates are indicated below the graph. Mean with standard deviation (SD) is shown. P values were derived from one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s ad hoc test. Source data are available online for this figure.